Searching the Help
To search for information in the Help, type a word or phrase in the Search box. When you enter a group of words, OR is inferred. You can use Boolean operators to refine your search.
Results returned are case insensitive. However, results ranking takes case into account and assigns higher scores to case matches. Therefore, a search for "cats" followed by a search for "Cats" would return the same number of Help topics, but the order in which the topics are listed would be different.
| Search for | Example | Results |
|---|---|---|
| A single word | cat
|
Topics that contain the word "cat". You will also find its grammatical variations, such as "cats". |
|
A phrase. You can specify that the search results contain a specific phrase. |
"cat food" (quotation marks) |
Topics that contain the literal phrase "cat food" and all its grammatical variations. Without the quotation marks, the query is equivalent to specifying an OR operator, which finds topics with one of the individual words instead of the phrase. |
| Search for | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Two or more words in the same topic |
|
|
| Either word in a topic |
|
|
| Topics that do not contain a specific word or phrase |
|
|
| Topics that contain one string and do not contain another | ^ (caret) |
cat ^ mouse
|
| A combination of search types | ( ) parentheses |
|
- Developing Generic Database Adapters
- Generic Database Adapter Overview
- TQL Queries for the Generic Database Adapter
- Reconciliation
- Hibernate as JPA Provider
- Prepare for Adapter Creation
- Prepare the Adapter Package
- Configure the Adapter – Minimal Method
- Configure the Adapter – Advanced Method
- Implement a Plugin
- Deploy the Adapter
- Edit the Adapter
- Create an Integration Point
- Create a View
- Calculate the Results
- View the Results
- View Reports
- Enable Log Files
- Use Eclipse to Map Between CIT Attributes and Database Tables
- Adapter Configuration Files
- Out-of-the-Box Converters
- Plugins
- Configuration Examples
- Adapter Log Files
- External References
- Troubleshooting and Limitations
Hibernate as JPA Provider
Hibernate is an object-relational (OR) mapping tool, which enables mapping Java classes to tables over several types of relational databases (for example, Oracle and Microsoft SQL Server). For details, see Functional Limitations.
In an elementary mapping, each Java class is mapped to a single table. More advanced mapping enables inheritance mapping (as can occur in the
Other supported features include mapping a class to several tables, support for collections, and associations of types one-to-one, one-to-many, and many-to-one. For details, see Associations below.
For our purposes, there is no need to create Java classes. The mapping is defined from the
This section also includes the following topics:
The following examples describe object-relational mapping:
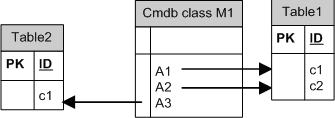
Example of One
Class M1, with attributes A1, A2, and A3, is mapped to table 1 columns c1, c2, and c3. This means that any M1 instance has a matching row in table 1.

Example of One
Example of Inheritance:
This case is used in the
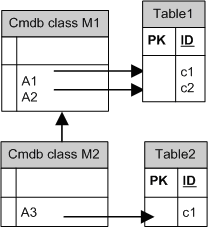
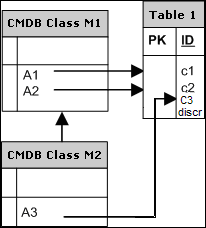
Example of Single Table Inheritance with Discriminator:
An entire hierarchy of classes is mapped to a single database table, whose columns comprise a super-set of all attributes of the mapped classes. The table also contains an additional column (Discriminator), whose value indicates which specific class should be mapped to this entry.
There are three types of associations: one-to-many, many-to-one and many-to-many. To connect between the different database objects, one of these associations must be defined by using a foreign key column (for the one-to-many case) or a mapping table (for the many-to-many case).
As the JPA schema is very extensive, a streamlined XML file is provided to make it easier to define associations.
The use case for using this XML file is as follows: Federated data is modeled into one federated class. This class has many-to-one relations to a non-federated