Searching the Help
To search for information in the Help, type a word or phrase in the Search box. When you enter a group of words, OR is inferred. You can use Boolean operators to refine your search.
Results returned are case insensitive. However, results ranking takes case into account and assigns higher scores to case matches. Therefore, a search for "cats" followed by a search for "Cats" would return the same number of Help topics, but the order in which the topics are listed would be different.
| Search for | Example | Results |
|---|---|---|
| A single word | cat
|
Topics that contain the word "cat". You will also find its grammatical variations, such as "cats". |
|
A phrase. You can specify that the search results contain a specific phrase. |
"cat food" (quotation marks) |
Topics that contain the literal phrase "cat food" and all its grammatical variations. Without the quotation marks, the query is equivalent to specifying an OR operator, which finds topics with one of the individual words instead of the phrase. |
| Search for | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Two or more words in the same topic |
|
|
| Either word in a topic |
|
|
| Topics that do not contain a specific word or phrase |
|
|
| Topics that contain one string and do not contain another | ^ (caret) |
cat ^ mouse
|
| A combination of search types | ( ) parentheses |
|
Work with Resource Bundles
A resource bundle is a file that takes a properties extension (*.properties). A properties file can be considered a dictionary that stores data in the format of key = value. Each row in a properties file contains one key = value association. The main functionality of a resource bundle is to return a value by its key.
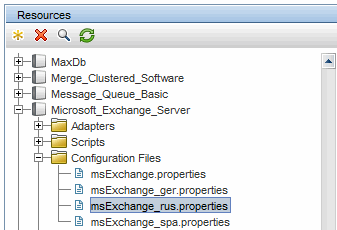
Resource bundles are located on the Probe machine: C:\hp\UCMDB\DataFlowProbe\runtime\probeManager\discoveryConfigFiles. They are downloaded from the
When discovering a destination, DFM usually needs to parse text from command output or file content. This parsing is often based on a regular expression. Different languages require different regular expressions to be used for parsing. For code to be written once for all languages, all language-specific data must be extracted to resource bundles. There is a resource bundle for each language. (Although it is possible for a resource bundle to contain data for different languages, in DFM each resource bundle contains data for one language only.)
The Jython script itself does not include hard coded, language-specific data (for example, language-specific regular expressions). The script determines the language of the remote system, loads the proper resource bundle, and obtains all language-specific data by a specific key.
In DFM, resource bundles take a specific name format: <base_name>_<language_identifier>.properties, for example, langNetwork_spa.properties. (The default resource bundle takes the following format: <base_name>.properties, for example, langNetwork.properties.)
The base_name format reflects the intended purpose of this bundle. For example, langMsCluster means the resource bundle contains language-specific resources used by the MS Cluster jobs.
The language_identifier format is a 3-letter acronym used to identify the language. For example, rus stands for the Russian language and ger for the German language. This language identifier is included in the declaration of the Language object.