Searching the Help
To search for information in the Help, type a word or phrase in the Search box. When you enter a group of words, OR is inferred. You can use Boolean operators to refine your search.
Results returned are case insensitive. However, results ranking takes case into account and assigns higher scores to case matches. Therefore, a search for "cats" followed by a search for "Cats" would return the same number of Help topics, but the order in which the topics are listed would be different.
| Search for | Example | Results |
|---|---|---|
| A single word | cat
|
Topics that contain the word "cat". You will also find its grammatical variations, such as "cats". |
|
A phrase. You can specify that the search results contain a specific phrase. |
"cat food" (quotation marks) |
Topics that contain the literal phrase "cat food" and all its grammatical variations. Without the quotation marks, the query is equivalent to specifying an OR operator, which finds topics with one of the individual words instead of the phrase. |
| Search for | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Two or more words in the same topic |
|
|
| Either word in a topic |
|
|
| Topics that do not contain a specific word or phrase |
|
|
| Topics that contain one string and do not contain another | ^ (caret) |
cat ^ mouse
|
| A combination of search types | ( ) parentheses |
|
Asset Field Parameters
Calculated Fields
Calculated fields can be automatically populated from data extracted from text files, the Windows registry, environment variables and so on.
This field is set up to read the value contained in an operating system’s environment string. For example, you may have the Host Name or SMS ID stored in an environment variable and want this to be automatically picked up by the scanner.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Enter the name of an environment variable | Examples of environment variables: TEMP and PATH. |
This type of field searches the Windows registry for the defined key and makes an automatic entry of the key value. This extract field is applicable to Windows only.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
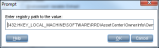
Enter registry path to the value |
The full path to the registry value you want to have in this field in the form RegistryKey\Value. Example: To find out whether the Screen Saver is active on the system, you can use the following registry extract field:
The registry does not allow the backslash ("\") character in the RegistryKey. However, it can be used in Value. If the backslash character is contained in the Value name, it must be escaped. For example, if Value is "a\b", it must be specified as follows:
In Windows, the paths to various registry values can be found by viewing the content in the Registry Editor. For more information about the Registry Editor refer to the Windows documentation. In 64-bit versions of Windows, portions of the registry entries are stored separately for 32-bit applications and 64-bit applications and mapped into separate logical registry views using the registry redirector and registry reflection. This is because the 64-bit version of an application may use different registry keys and values than the 32-bit version. There are also shared registry keys that are not redirected or reflected. Because the Universal Discovery Windows scanner is a 32-bit application, by default, the scanner only reads the 32-bit portion of the registry.To access the 64-bit registry portion in 64-bit versions of Windows, the scanner supports the following prefixes: Note The prefix includes the colon (:).
If no prefix is given, the scanner reads the 32-bit registry value only. The actual registry value path should follow the prefix, as shown in the following example: |
This field searches a named text file for a defined character string and makes an automatic entry of the characters between the search string and the end of the line.
This field type is normally used for the Asset Number field. This is used to extract the asset number from the file Asset.bat on the line containing the text: SET ASSETNO=
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
File Name |
The name of the file (and the file path) that the information is to be extracted from. Note:
|
| Search |
Determines what information is to be extracted.
Note
|
Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) is a component of the Microsoft Windows operating system that provides management information.
Some data on Windows operating systems is only available via the WMI interface. This type of field allows the scanner to be configured to extract and store specific pieces of WMI data. The Windows scanner populates this field on computers where WMI is enabled.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Query |
Windows Management Instrumentation Query Language (WQL) is a subset of SQL that is used to make data queries inside WMI. WQL Query. The following example of a WQL query collects the name and the frequency properties of the installed processor: For example, For more information about WMI and WQL refer to the Microsoft MSDN website.
|
| Options |
|
| Output Properties |
Enables you to add a property whose value is required in the asset field. The WQL query returns an instance of the WMI class which can have many properties. The required properties need to be specified manually. For example: select * from Win32_Processor This returns all properties for processor, but if Name is required, it should be specified in the Output Properties box.
|
Derived Fields
Derived fields have dependencies on the data of other types of fields. That is, the data they contain is derived from other fields.
The Sequence field enables you to define a sequence of up to ten asset or hardware fields. Each of these fields returns a value depending on the machine or environment running. The value returned as the result of the sequence field is the first of these fields containing a non-blank value.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Field Sequence |
The sequence of the field. Expand the tree on the right and drag a field to the File Name list on the left. |
| Ignore Strings |
Used to specify a set of values that are known to be incorrect, fake, or unwanted. These values should be ignored. For example, when specifying a MAC address as one of the hardware fields in a sequence, you can designate the known fake MAC addresses in the Ignore Strings so that they can be filtered out. A blank field can be defined based on either of the following two criteria:
|
These fields can combine up to five asset or hardware fields into a single field. This is particularly useful for the Description field.
The combination field is made up by string substitution.
For a detailed example on setting up a Combination type asset field, see How to Set Up Asset Fields for Data Collection - Example.
| Parameter | Description | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Master substitution string |
The template substitution string that makes up the combination field. This string replaces the percent values (for example, %1) with the appropriate hardware or asset item. Syntax: Use the percentage symbol followed by a number. Note You can also specify some text before or after the percent notation which will be a constant part of the value of the field. Examples
|
||||||||||||
| Definitions |
Displays the fields selected from the Fields tree (on the right) to be used in the substitution string. The list can contain up to five index entries (represented as %1, %2, %3, %4 and %5). |
||||||||||||
| <Right-click menu> |
|
These fields allow the definition of multiple types of data sources to provide an automatic entry depending on the scanner used and the operating system being scanned.
This type of asset field is useful in situations when you want to scan multiple operating systems but want to collect the same piece of information for each from different sources.
For example, the data can be extracted from the registry on Windows or from a file on UNIX and Mac OS X.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
Field Index |
|
| Fields Referred to | Fields selected from the Fields tree (on the right) to be included in this definition.Can be any existing asset field or any hardware/configuration field (except hardware fields where multiple values may be collected, such as CPU type or IP address). |
| Fields tree | Displays the available fields. |





 . Enables you to add an output property.
. Enables you to add an output property. . Enables you to remove the selected output property.
. Enables you to remove the selected output property. .
. .
.