Searching the Help
To search for information in the Help, type a word or phrase in the Search box. When you enter a group of words, OR is inferred. You can use Boolean operators to refine your search.
Results returned are case insensitive. However, results ranking takes case into account and assigns higher scores to case matches. Therefore, a search for "cats" followed by a search for "Cats" would return the same number of Help topics, but the order in which the topics are listed would be different.
| Search for | Example | Results |
|---|---|---|
| A single word | cat
|
Topics that contain the word "cat". You will also find its grammatical variations, such as "cats". |
|
A phrase. You can specify that the search results contain a specific phrase. |
"cat food" (quotation marks) |
Topics that contain the literal phrase "cat food" and all its grammatical variations. Without the quotation marks, the query is equivalent to specifying an OR operator, which finds topics with one of the individual words instead of the phrase. |
| Search for | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Two or more words in the same topic |
|
|
| Either word in a topic |
|
|
| Topics that do not contain a specific word or phrase |
|
|
| Topics that contain one string and do not contain another | ^ (caret) |
cat ^ mouse
|
| A combination of search types | ( ) parentheses |
|
Problem workflow
Problem management investigates incidents, determines causes, and provides solutions. It is a process that minimizes the impact on customers of errors in infrastructure, services and external events. The focus is to diagnose and rectify faults in the IT infrastructure, to obtain the highest possible stability in IT Service Delivery.
In Service Management, a workflow is the end-to-end process of problem management, from the problem creation to the problem closure. The Service Management problem workflow, includes all necessary steps to log and resolve a problem, and is a best practice for problem management, reflecting ITILv3 and Micro Focus process recommendations.
The building blocks of the workflow are metaphases, phases and transitions. Service Management displays a graphic view of the workflow where you can see the current phase and the transitions that connect the current phase to all other phases.
The Problem Management workflow contains four metaphases and six phases that lead to closure. When you update a record or assign a new status, the record can transition from one process phase to the next automatically.
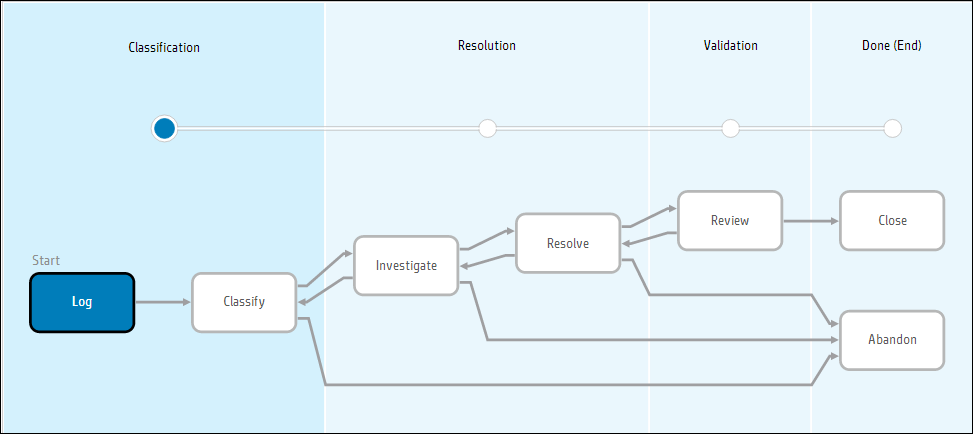
Metaphase: Classification
| Phase | Transition | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Log | Automatic |
The analyst enters detailed information about the problem. Next phase: Classify |
| Classify | Manual or automatic |
The Problem Manager verifies the information provided, performs an initial analysis, and selects a category for the problem. The Problem Manager also assigns the problem to a Problem Analyst. Next phase: Investigate or Abandon |
Metaphase: Resolution
The Problem Manager assigns the problem to the Problem Analyst. The Problem Analyst analyzes the problem to identify the root cause, and searches for a fix or workaround. The Problem Analyst takes the actions required to fix the problem.
| Phase | Transition |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Investigate |
Manual |
The Problem Analyst analyzes the problem to identify the root cause, and searches for a fix or workaround. Next phase: Resolve or Abandon |
| Resolve | Automatic |
The Problem Analyst develops and tests a plan detailing all the corrective actions that must be performed to fix the problem. The plan is then implemented. Next phase: Investigate, Review, or Abandon |
Metaphase: Validation
| Phase | Transition |
Description |
|---|---|---|
| Review | Manual |
The Problem Analyst reviews the history of the problem and its resolution, and makes a final decision as to whether or not it has been corrected. The Problem Analyst also sets the completion code value, and describes the fix or workaround. In addition, the Problem Analyst considers if steps can be taken to improve the process, and determines whether to store a record of the problem and its resolution in knowledge management. Next phase: Resolve or Close |
Metaphase: Done (End)
The analyst can close the problem after recording all related information. In addition, in appropriate circumstances the analyst can abandon a problem, meaning the record is no longer active.
| Phase | Transition |
Description |
|---|---|---|
| Close | None |
The problem is closed. Next phase: None |
| Abandon | None |
The problem is abandoned and is inactive. Next phase: None |
Related topics