Searching the Help
To search for information in the Help, type a word or phrase in the Search box. When you enter a group of words, OR is inferred. You can use Boolean operators to refine your search.
Results returned are case insensitive. However, results ranking takes case into account and assigns higher scores to case matches. Therefore, a search for "cats" followed by a search for "Cats" would return the same number of Help topics, but the order in which the topics are listed would be different.
| Search for | Example | Results |
|---|---|---|
| A single word | cat
|
Topics that contain the word "cat". You will also find its grammatical variations, such as "cats". |
|
A phrase. You can specify that the search results contain a specific phrase. |
"cat food" (quotation marks) |
Topics that contain the literal phrase "cat food" and all its grammatical variations. Without the quotation marks, the query is equivalent to specifying an OR operator, which finds topics with one of the individual words instead of the phrase. |
| Search for | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Two or more words in the same topic |
|
|
| Either word in a topic |
|
|
| Topics that do not contain a specific word or phrase |
|
|
| Topics that contain one string and do not contain another | ^ (caret) |
cat ^ mouse
|
| A combination of search types | ( ) parentheses |
|
- Integration Studio
- Integration in a Multi-Tenancy Environment
- How to Work with Federated Data
- How to Work with Population Jobs
- How to Work with Data Push Jobs
- How to Set Up an Integration Point
- How to Save an Integration Point Configuration as an Adapter Default
- How to Remove Adapter Defaults
- How to Deploy a Package to a Remote Data Repository
- How to Configure Probe IP Ranges with Active Directory
- Integration Studio User Interface
- Limitations
How to Work with Population Jobs
This task explains how to schedule population jobs and select the queries that are used to populate the
-
Set up the integration to populate the data. For details, see How to Set Up an Integration Point.
-
In the Integration Point pane, right-click the integration, and select Reconciliation Priority Manager from the shortcut menu. For more details, see Reconciliation Priority Window.
-
Population jobs are set to run according to a default schedule setting. However, you can manually run the integration at any time from the Integration Jobs pane. For user interface details, see Integration Jobs Pane.
Select the job.
-
To synchronize all data for the first time, click the Full Synchronization
 button.
button. -
To synchronize only the data changes since the job last ran, click the Delta Synchronization
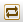 button.
button.
- If CIs in a population job fail, the query is displayed in the Query Status tab as Completed with a warning symbol
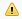 . You can drill down to see the errors that occurred and the CIs affected. This error data is saved in the system. When the job runs again to synchronize changes, UCMDB remembers the failed CIs and repopulates these as well.
. You can drill down to see the errors that occurred and the CIs affected. This error data is saved in the system. When the job runs again to synchronize changes, UCMDB remembers the failed CIs and repopulates these as well. -
If, since the last synchronization, you have changed a TQL query (other than changes to conditions on existing nodes), click the Clear Probe Results Cache
 button to ensure that the next run of the job is a full synchronization.
button to ensure that the next run of the job is a full synchronization. -
High Availability environment: If a population job is running, and the UCMDB Server responsible for write requests becomes unavailable or is changed, the job fails. You can wait for the next invocation of the job schedule, or alternatively rerun the population job manually.
- For ResultTreeNodes (RTNs) coming from external sources, their isDeleted attribute setting will not be overridden by the mapping process. For example, if one RTN, which has isDeleted attribute set true, comes from SM, using a population job, it will be deleted even if the mapping processing changes isDeleted to false.
-
-
Build a view of the population results.
For details about viewing the populated data, see Working with Views in IT Universe Manager.
-
View instances in IT Universe Manager.
For details about viewing the CI instances, see Working with Views in IT Universe Manager.
-
You can view reports about the integration in the Modeling Studio. For details see Reports.
We welcome your comments!
To open the configured email client on this computer, open an email window.
Otherwise, copy the information below to a web mail client, and send this email to cms-doc@microfocus.com.
Help Topic ID:
Product:
Topic Title:
Feedback: