Searching the Help
To search for information in the Help, type a word or phrase in the Search box. When you enter a group of words, OR is inferred. You can use Boolean operators to refine your search.
Results returned are case insensitive. However, results ranking takes case into account and assigns higher scores to case matches. Therefore, a search for "cats" followed by a search for "Cats" would return the same number of Help topics, but the order in which the topics are listed would be different.
| Search for | Example | Results |
|---|---|---|
| A single word | cat
|
Topics that contain the word "cat". You will also find its grammatical variations, such as "cats". |
|
A phrase. You can specify that the search results contain a specific phrase. |
"cat food" (quotation marks) |
Topics that contain the literal phrase "cat food" and all its grammatical variations. Without the quotation marks, the query is equivalent to specifying an OR operator, which finds topics with one of the individual words instead of the phrase. |
| Search for | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Two or more words in the same topic |
|
|
| Either word in a topic |
|
|
| Topics that do not contain a specific word or phrase |
|
|
| Topics that contain one string and do not contain another | ^ (caret) |
cat ^ mouse
|
| A combination of search types | ( ) parentheses |
|
Field selection rule examples
The following examples demonstrate how to formulate rules for each of the field selection rule templates:
-
For the field parameter, select a field from the drop-down list.
-
For the title parameter, enter the title to be displayed in the user interface.
-
For the all records parameter, you define filters to control the type of data accepted in the selected field. Click the Add Item button, which displays two boxes. In the first box, select a field from the drop-down list. In the second, select IN or NOT IN from the drop-down list. A third box appears. Enter an Expression Language phrase that returns the data accepted in the selected field. For a full list of Expression Language functions, see Expression Language functions and syntax.
Click Add Item again to add another row and define another filter.
-
When the rule runs, it defines the type of data accepted in the selected field according to the specified filters.
Example: In the rule IncidentAssigneeFilter in Incident Management, the field AssignedPerson is defined to accept the title set Group Members and to accept data types according to the following filter set: for the first value, select PersonToGroup.Id. For the second value, select IN. For the third value, enter the following Expression Language phrase: ${entity.AssignedGroup.Id}.
Note
- You can define more than one field selection rule for the same field. The available values for the field based on each of the filters are displayed in a separate section of the drop-down for each filter.
- At least one of the fields selected for the filter must be a searchable field.
-
For the field parameter, select a field from the drop-down list.
-
For the title parameter, enter the name of the subsection in the drop-down list to be displayed in the user interface.
-
For the name parameter, select the routing definition name from the drop-down list.
-
For the parameters parameter, there is one parameter for each lane of the routing definition. For each parameter, enter an Expression Language phrase that returns the required value. For a full list of Expression Language functions, see Expression Language functions and syntax.
-
When the rule runs, it defines the values available to be selected for the selected group field. The values are determined based on the path defined in the selected routing definition.
For an example of the business rule, see Routing definition use case - defining suggested values.
-
For the field1 parameter, select a field from the drop-down list.
-
For the field2 parameter, select a field from the drop-down list.
-
For the mapping definition parameter, select a value from the list on the left, and then click the box on the right to open a list of secondary values. Select the required secondary values for the selected primary value. You can select multiple secondary values.
Select another primary value on the left and select the required secondary values for that value.
-
For the default values parameter, click the box to open a list of values. These represent the secondary values for the remaining primary values. Select the required values from the list. This parameter is optional.
-
When the rule runs, it defines the values available to be selected for each field1 option from among the field2 values, according to the specified mapping. For the field1 options that were not specified in the mapping, the field2 values selected in the default values parameter are available. If no value is selected for the default values parameter, the field options not selected in the mapping have no available values.
Example:
-
Select Environment as field1 and Business criticality as field2.
-
The dialog box for the mapping definition displays a list of environment options on the left side (Production, Test, Staging, etc.). Select Production and then click on the right side of the dialog box.
-
A list of business criticality values is displayed. Select Medium, High, and Very high.
-
Next select Test on the left side and then click on the right side and select Low, Medium, and High. Click OK.
-
For the default values parameter, click in the box to display a list of business criticality values. Select Very low, Low, and Medium. Click OK.
The rule defines the following options for the user:
- When Production is selected as the environment, the business criticality drop-down list displays Medium, High, and Very high as the available values.
- When Test is selected as the environment, the business criticality drop-down list displays Low, Medium, and High as the available values.
- When any other environment is selected, the business criticality drop-down list displays Very low, Low, and Medium as the available values.
-
For the users parameter, select one of the following options:
-
Simple Mode. Enter the required text in the text box.
-
Expression Language. Enter an Expression Language phrase that returns the required text.
Click the Expression Language
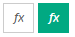 button to toggle between these options. When the button is selected (green), the field is in Expression Language mode. When it is not selected (white), the field is in Simple mode. For a full list of Expression Language functions, see Expression Language functions and syntax.
button to toggle between these options. When the button is selected (green), the field is in Expression Language mode. When it is not selected (white), the field is in Simple mode. For a full list of Expression Language functions, see Expression Language functions and syntax. -
-
For the field parameter, select a field from the drop-down list.
-
For the title parameter, enter the name of the subsection in the drop-down list to be displayed in the user interface.
-
When the rule runs, it displays the selected users under the specified heading.
Example:
The following rule is in Request management:

Note
- All of the rules can be formulated with the "If...Then" option, which includes an expression parameter for the condition. Make sure to enter an Expression Language phrase that returns a Boolean value.
- Field selection rules are only available for the Rendering forms process event.
-
To display users but not contacts in a drop-down list, you can define the field selection business rule in the workflow according to the following filter set:
- For the first value, select isMaasUser.
- For the second value, select IN.
- For the third value, enter the following Expression Language phrase: ${true}.