Searching the Help
To search for information in the Help, type a word or phrase in the Search box. When you enter a group of words, OR is inferred. You can use Boolean operators to refine your search.
Results returned are case insensitive. However, results ranking takes case into account and assigns higher scores to case matches. Therefore, a search for "cats" followed by a search for "Cats" would return the same number of Help topics, but the order in which the topics are listed would be different.
| Search for | Example | Results |
|---|---|---|
| A single word | cat
|
Topics that contain the word "cat". You will also find its grammatical variations, such as "cats". |
|
A phrase. You can specify that the search results contain a specific phrase. |
"cat food" (quotation marks) |
Topics that contain the literal phrase "cat food" and all its grammatical variations. Without the quotation marks, the query is equivalent to specifying an OR operator, which finds topics with one of the individual words instead of the phrase. |
| Search for | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Two or more words in the same topic |
|
|
| Either word in a topic |
|
|
| Topics that do not contain a specific word or phrase |
|
|
| Topics that contain one string and do not contain another | ^ (caret) |
cat ^ mouse
|
| A combination of search types | ( ) parentheses |
|
- Developing Generic Adapters
- Instance Sync
- Achieving Data Push using the Generic Adapter
- Achieving Data Population using the Generic Adapter
- Achieving Data Federation using the Generic Adapter
- Reconciliation
- Generic Adapter API
- Resource Locator APIs
- Create a Generic Adapter Package
- Differences Between Push and Population Mapping
- Generic Adapter Log Files
- Adapters Using the Generic Adapter Framework
- Generic Adapter XML Schema Reference
Differences Between Push and Population Mapping
Although both push and population mapping files have the same underlying XML schema, the files have slightly different interpretations. For more information, see Generic Adapter XML Schema Reference.
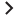
In the following push mapping example, the interpretation is: take the results of the “Computer Push” TQL query (run in UCMDB) and present in the Root tree structure, and create the amComputer entity which will later on be sent to AM.
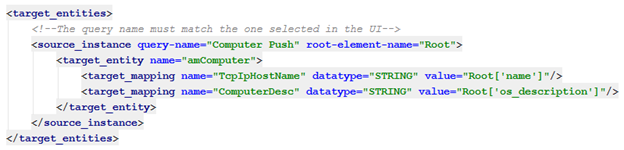
In the following population mapping example, the interpretation is: take the results of the “Nodes Population” TQL query (run in the external system) and present in the PC tree structure, and create the UCMDB Root entity (of type Node; as indicated by the TQL query), which will later be added in UCMDB.
We welcome your comments!
To open the configured email client on this computer, open an email window.
Otherwise, copy the information below to a web mail client, and send this email to cms-doc@microfocus.com.
Help Topic ID:
Product:
Topic Title:
Feedback: