Searching the Help
To search for information in the Help, type a word or phrase in the Search box. When you enter a group of words, OR is inferred. You can use Boolean operators to refine your search.
Results returned are case insensitive. However, results ranking takes case into account and assigns higher scores to case matches. Therefore, a search for "cats" followed by a search for "Cats" would return the same number of Help topics, but the order in which the topics are listed would be different.
| Search for | Example | Results |
|---|---|---|
| A single word | cat
|
Topics that contain the word "cat". You will also find its grammatical variations, such as "cats". |
|
A phrase. You can specify that the search results contain a specific phrase. |
"cat food" (quotation marks) |
Topics that contain the literal phrase "cat food" and all its grammatical variations. Without the quotation marks, the query is equivalent to specifying an OR operator, which finds topics with one of the individual words instead of the phrase. |
| Search for | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Two or more words in the same topic |
|
|
| Either word in a topic |
|
|
| Topics that do not contain a specific word or phrase |
|
|
| Topics that contain one string and do not contain another | ^ (caret) |
cat ^ mouse
|
| A combination of search types | ( ) parentheses |
|
Manual Link Population
The Generic Adapter achieves the population of links by defining (mapping) the three entities required by a link:
- the Link entity
- the Link’s End 1 entity
- the Link’s End 2 entity
Let’s analyze the mapping example shown in Population Mapping Files. In this case, we are populating three entity types in UCMDB: Nodes, Running Software, and the Composition link between them. Because we want to populate a link (the link named RootLink of type Composition), we also need to map the two link ends. Thus, from looking at the TQL query we see that the entities that need mapping are Node (end 1) and Software (end 2). The way the Generic Adapter framework understands the link structure is by looking at the created entity’s element name and definition in the TQL query. Because the population job must also bring instances of Node and Running Software, the needed ends’ mapping is already in place.
Types of Link Population
There are two types of link population situations:
-
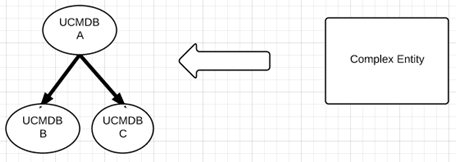
Decomposing a complex external entity in multiple related UCMDB entities
In this case, a complex external entity such as PC is converted into the UCMDB Node and Running Software types, which need to be linked by a Composition link. This type of link only exists in the context of UCMDB.
-
Links between complex external entities
In this case, we need to model a link between two complex external entities such as PCs.
We welcome your comments!
To open the configured email client on this computer, open an email window.
Otherwise, copy the information below to a web mail client, and send this email to cms-doc@microfocus.com.
Help Topic ID:
Product:
Topic Title:
Feedback: