Searching the Help
To search for information in the Help, type a word or phrase in the Search box. When you enter a group of words, OR is inferred. You can use Boolean operators to refine your search.
Results returned are case insensitive. However, results ranking takes case into account and assigns higher scores to case matches. Therefore, a search for "cats" followed by a search for "Cats" would return the same number of Help topics, but the order in which the topics are listed would be different.
| Search for | Example | Results |
|---|---|---|
| A single word | cat
|
Topics that contain the word "cat". You will also find its grammatical variations, such as "cats". |
|
A phrase. You can specify that the search results contain a specific phrase. |
"cat food" (quotation marks) |
Topics that contain the literal phrase "cat food" and all its grammatical variations. Without the quotation marks, the query is equivalent to specifying an OR operator, which finds topics with one of the individual words instead of the phrase. |
| Search for | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Two or more words in the same topic |
|
|
| Either word in a topic |
|
|
| Topics that do not contain a specific word or phrase |
|
|
| Topics that contain one string and do not contain another | ^ (caret) |
cat ^ mouse
|
| A combination of search types | ( ) parentheses |
|
- Administer
- User and user group setup and security
- SA Core and component security
- Multimaster Mesh administration
- Facility administration
- Satellite administration
- SA remote communications administration
- SA maintenance
- Monitoring SA Core components
- Diagnostic tests
- Log files
- SA notifications
- Global Shell: Windows subauthentication package
- Permissions reference
- Managed platform support
- Reports
- Content utilities
- Audit and compliance
- SA Provisioning
- Backup and Restore Best Practices
- SA management console
- HPSA_High_Availability
- SA UEFI Secure-Boot Server Provisioning
- RPM Remediation Best Practice - Using the mrc_calc Tool
- SA Agents in the public cloud
- Best Practices for Importing RHEL 7 Content
- Managed OS Platforms as Content in SA
- glibc Vulnerability: CVE-2015-0235
SA Agents in the public cloud
This section provides information about SA Agents in the public cloud, how to set up and deploy a Satellite for Amazon Web Services (AWS), and how to manage your cloud instances with
SA Agents.
For this implementation, we assume you have HPE SA up and running. Each component must be verified to work individually and within HPE SA. If you do not have HPE SA deployed, see the Server Automation Install section.
Using SA to agent-manage servers in private and public clouds enables SA power and functionality in each cloud instance. We recommend deploying and using a satellite, because cloud instances that are hosted by cloud service providers are similar to servers at a remote site.
A satellite installation typically consists of, at minimum, a satellite gateway and a software repository cache and allows you to fully manage servers at a remote facility. The software repository cache contains local copies of software packages to be installed on managed servers in the satellite, while the satellite gateway handles communication with the primary core.
An agent-managed instance can communicate with an SA Satellite to run patching, software management, application configuration, audit, and remediation. You can optionally install the OS provisioning boot server and media server on the Satellite host to support remote OS provisioning and reprovisioning.
SA Agents in the public cloud implementation
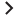
The implementation described in this section consists of an SA Core within the corporate firewall that is connected to an SA Satellite on an AWS instance. We recommend using the Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) networking service, which enables you to provision a private, isolated section of the AWS cloud where you can launch AWS resources in a virtual network.
Environment
The scenario uses VPC with a single private subnet and a virtual private gateway to enable communication with the network over an IPsec VPN tunnel. There is no Internet gateway. This scenario can be used to extend a network into the cloud without exposing a network to the Internet. A Satellite is connected directly to the SA Core, and the Core is connected to AWS (see figure below). Cloud Provider: AWS.
Agent - Manage instances through a satellite
This section describes prerequisites and steps needed to agent-manage instances through a Satellite.
- Establish a Connection to AWS from Your Network
- Install a Satellite on an AWS Instance
- Install SA Agents on Instances
Establish a connection to AWS from your network
- Create and configure the Amazon VPC as described here: http://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonVPC/latest/UserGuide/VPC_Scenario4.html
- Open the required SA ports in the VPC’s default security group, as shown in Table 1
(see the Server Automation Install Guide for more details).
Table 1. Required SA Ports
|
Inbound ports |
Outbound ports |
|---|---|
|
- |
22 (SSH) to copy the Satellite distribution to the cloud. |
|
1002 for SA Agent communication. |
1002 for SA Agent communication. |
|
- |
1003 and 1006 for the Software Repository Cache. |
|
2001 for the SA Satellite to communicate with the SA Core. |
2001 for the SA Satellite to communicate with the SA Core. |
|
3003 for the SA Satellite gateway installer. |
- |
|
- |
4040 for the gateway used by the Software Repository Cache. |
- Create a VPN connection between the VPC and your local network.
For information about VPNs that can be used to secure the connection and how to configure the virtual private gateway, see the Amazon Virtual Private Cloud Network Administrator Guide.
Install a Satellite on an AWS instance
- Create an AWS instance on which you can install the Satellite.
- In this implementation, Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 6.4x86_64 is used. For other supported platforms, see the Server Automation Support and Compatibility Matrix.
- Configure the iptables firewall to open the SA ports listed in Table 1.
- Copy the Satellite distribution to the Satellite server in AWS.
- Run Satellite prerequisite checks, and fix any issues.
- Copy the certificate and CDF file from the Core server to the Satellite server.
- Run the Satellite installer.
- Enable the SA Agent Installer on the Satellite by adding the following to the root user’s path:
- OpenSSH client
- telnet client (standard client that ships with Linux)
- rlogin (standard login that ships with Linux)
For more information about SA Satellite installation and deployment, see the Server Automation Install Guide.
Install SA Agents on Instances
For details about SA Agent installation, see the Server Automation User Guide.
For Linux instances, enable SSH password authentication and root login. For Windows instances, enable NETBIOS over TCP/IP.
The Satellite server needs to communicate to instances through the SA Agent Installer. To do this, for example, you may need to configure or disable the iptables firewall (in Linux) or the Windows Firewall.
- Configure the firewall as needed for your instance.
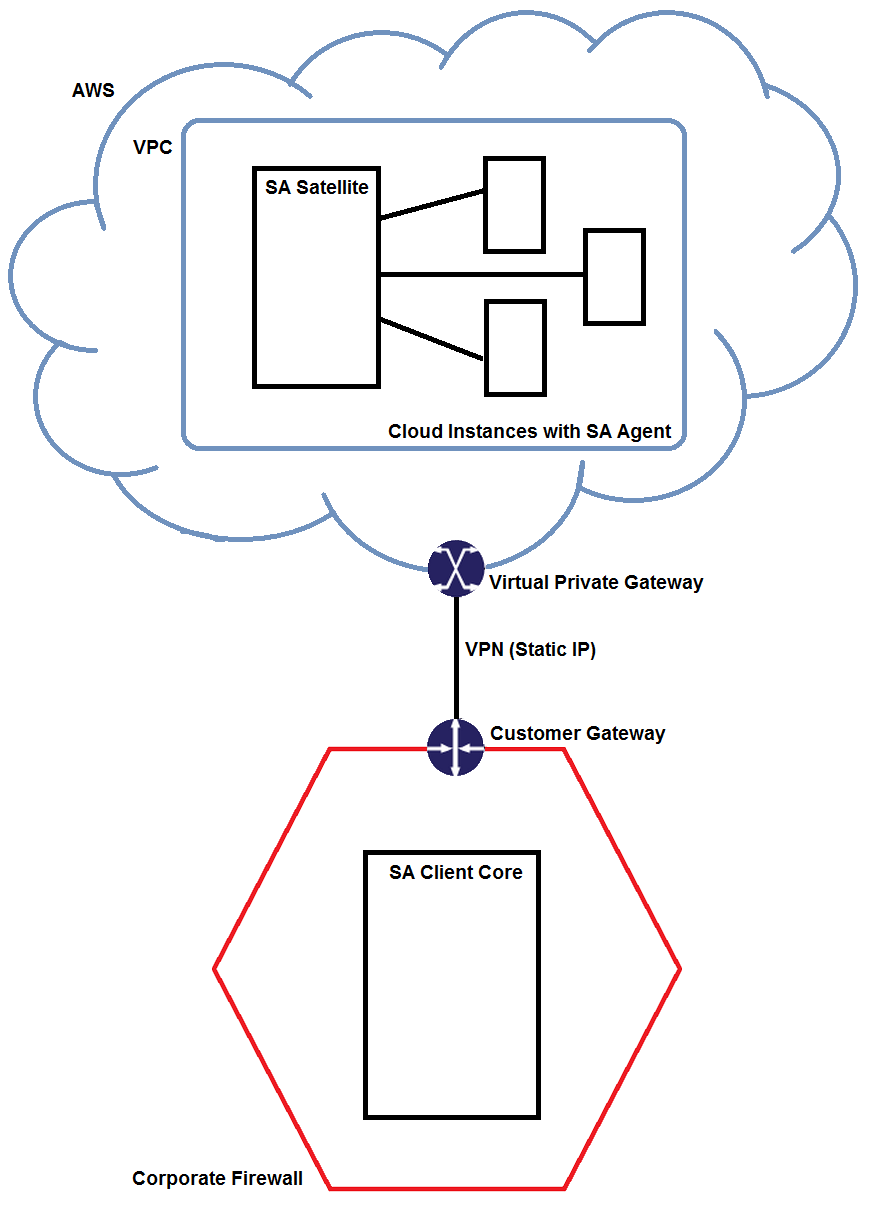
- Log in to the SA Client.
- Navigate to SA Agent Installation, and select the Satellite from the “Scan In” drop-down list.
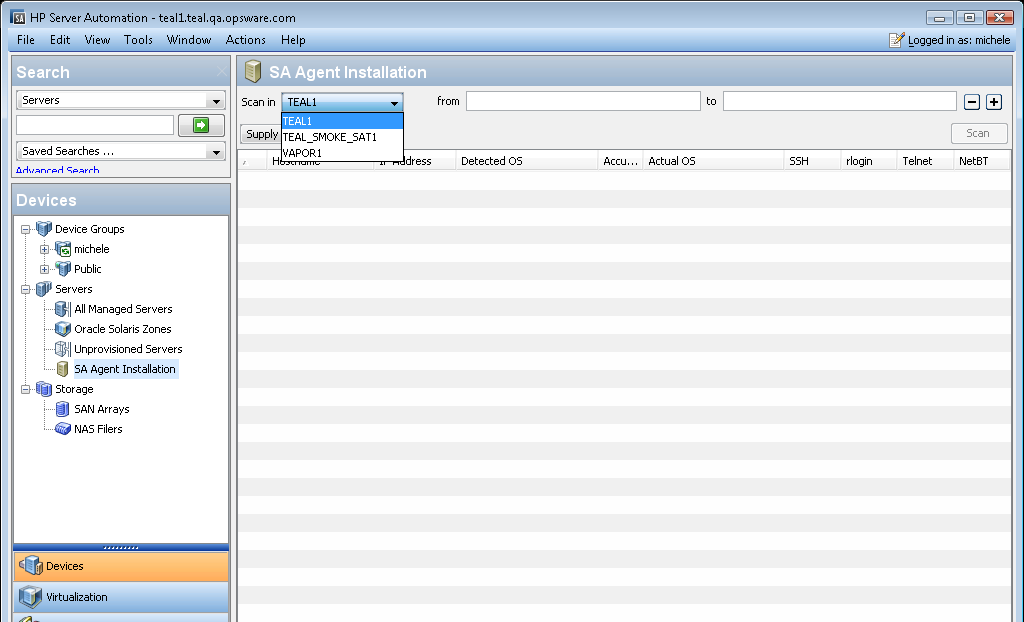
Figure 2 Select the Satellite to Scan In
- Scan in your private IP address range to discover agentless servers.
- Right-click each server on which you want to install SA Agent, and run the Agent Installer.
You are now ready to leverage SA in the public cloud. You can use the SA Documentation Library to find the latest version of the guides for your version of SA on the HPE Software Support Online (HPE Passport required).
We welcome your comments!
To open the configured email client on this computer, open an email window.
Otherwise, copy the information below to a web mail client, and send this email to hpe_sa_docs@hpe.com.
Help Topic ID:
Product:
Topic Title:
Feedback: