Searching the Help
To search for information in the Help, type a word or phrase in the Search box. When you enter a group of words, OR is inferred. You can use Boolean operators to refine your search.
Results returned are case insensitive. However, results ranking takes case into account and assigns higher scores to case matches. Therefore, a search for "cats" followed by a search for "Cats" would return the same number of Help topics, but the order in which the topics are listed would be different.
| Search for | Example | Results |
|---|---|---|
| A single word | cat
|
Topics that contain the word "cat". You will also find its grammatical variations, such as "cats". |
|
A phrase. You can specify that the search results contain a specific phrase. |
"cat food" (quotation marks) |
Topics that contain the literal phrase "cat food" and all its grammatical variations. Without the quotation marks, the query is equivalent to specifying an OR operator, which finds topics with one of the individual words instead of the phrase. |
| Search for | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Two or more words in the same topic |
|
|
| Either word in a topic |
|
|
| Topics that do not contain a specific word or phrase |
|
|
| Topics that contain one string and do not contain another | ^ (caret) |
cat ^ mouse
|
| A combination of search types | ( ) parentheses |
|
Patch management process
There are two main use cases in Solaris patching:
Patching selected servers
The following figure shows the steps required when you know which Solaris servers you want to patch and how you identify which patches those servers need. These steps include downloading and installing patches on your Solaris managed servers.
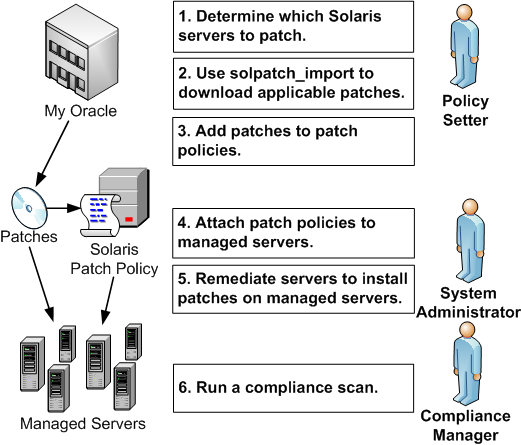
- A policy setter determines which Solaris servers need to be patched. For example, you may want to patch one specific Solaris server, all your servers running 5.10, all servers used by a particular department, or some other subset of your Solaris servers.
- A policy setter uses the
solpatch_importcommand to download the patches from Oracle that are required by the selected Solaris servers. The solpatch_import command determines which patches are required by the selected servers, resolves all patch dependencies, and includes all applicable patches. -
A policy setter adds the patches to a Solaris patch policy.
This step can be completed by running the
solpatch_importcommand as part of step 2 (excluding patch bundles) or you can manually place the Solaris patches into a patch policy by using the SA Client. -
A system administrator attaches the patch policies to managed servers.
Your system administrator can test the patches by attaching the patch policy to one or more test servers, to make sure they behave as expected. If problems occur, you can add or remove patches from the patch policy and then test the patches again. After testing is complete, your system administrator can attach the patch policy to all other Solaris servers.
-
A system administrator remediates patch policies. The remediate process installs the patches on your managed servers.
-
A compliance manager performs a compliance scan to determine which servers do not have the required patches installed.
Installing selected patches
The following figure shows the steps required when you know which Solaris patches you want to install and how you identify all dependent patches. These steps include downloading and installing one or more Solaris patches.

- A policy setter determines which Solaris patches need to be installed. You might be required to install one specific Solaris security patch or one specific patch that fixes a known problem on your managed servers.
- A policy setter uses the
solpatch_importcommand to download specific patches, patch clusters, or patch bundles from Oracle. -
A policy setter adds the patches to a Solaris patch policy.
This step can be completed by running the
solpatch_importcommand as part of step 2 (excluding patch bundles) or you can manually add the Solaris patches to a patch policy by using the SA Client. - A policy setter uses the
 button in the SA Client to resolve all dependencies for patches in the patch policy, including determining dependent patches, superseding patches, obsolete patches, incompatible patches, and withdrawn patches.
button in the SA Client to resolve all dependencies for patches in the patch policy, including determining dependent patches, superseding patches, obsolete patches, incompatible patches, and withdrawn patches. -
A system administrator attaches the patch policies to managed servers.
Your system administrator can test the patches by attaching the patch policy to one or more test servers, to make sure they behave as expected. If problems occur, you can add or remove patches from the patch policy and then test the patches again. After testing is complete, your system administrator can attach the patch policy to all other Solaris servers.
- A system administrator remediates patch policies. The remediate process installs the patches on your managed servers.
- A compliance manager performs a compliance scan to determine which servers do not have the required patches installed.
We welcome your comments!
To open the configured email client on this computer, open an email window.
Otherwise, copy the information below to a web mail client, and send this email to hpe_sa_docs@hpe.com.
Help Topic ID:
Product:
Topic Title:
Feedback: