Searching the Help
To search for information in the Help, type a word or phrase in the Search box. When you enter a group of words, OR is inferred. You can use Boolean operators to refine your search.
Results returned are case insensitive. However, results ranking takes case into account and assigns higher scores to case matches. Therefore, a search for "cats" followed by a search for "Cats" would return the same number of Help topics, but the order in which the topics are listed would be different.
| Search for | Example | Results |
|---|---|---|
| A single word | cat
|
Topics that contain the word "cat". You will also find its grammatical variations, such as "cats". |
|
A phrase. You can specify that the search results contain a specific phrase. |
"cat food" (quotation marks) |
Topics that contain the literal phrase "cat food" and all its grammatical variations. Without the quotation marks, the query is equivalent to specifying an OR operator, which finds topics with one of the individual words instead of the phrase. |
| Search for | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Two or more words in the same topic |
|
|
| Either word in a topic |
|
|
| Topics that do not contain a specific word or phrase |
|
|
| Topics that contain one string and do not contain another | ^ (caret) |
cat ^ mouse
|
| A combination of search types | ( ) parentheses |
|
View errata-based and channel-based policies in the SA Client
The suse_manager_import and smt_import tools allow you to create errata-based, erratum-based, and channel-based policies in the SA Client. After successfully running them, you can view the properties of errata-based, erratum-based, and channel-based policies in the SA Client. You can view properties such as the SA user who created the software policy, the date when it was created, the name, the description, the availability, the location of the policy in the Library, the operating systems applicable to the policy and the SA Client ID of the software policy. HPE recommend that you do not edit the policies created by the suse_manager_import and smt_import tools.
To view the properties of a software policy:
- From the navigation pane, select Library > By Folder.
- Select the SLES folder.
-
From the content pane, select the errata, channel, or content-based policy and open it. The policy window appears.
-
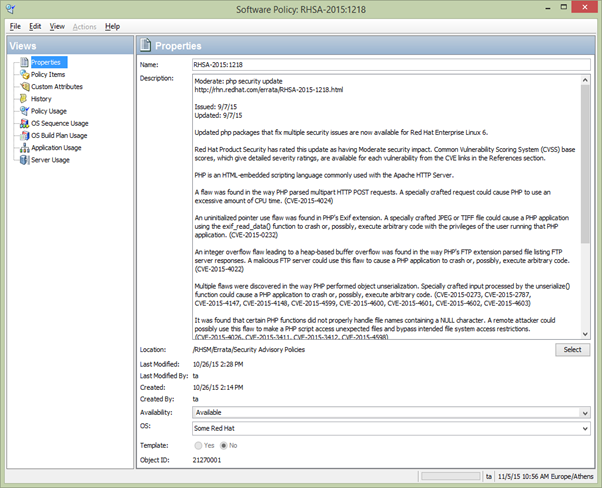
From the Views pane, select Properties. You can view the properties for the policy in the content pane.
-
Name: Contains the errata reference for the errata based software policy.
-
Description: Includes all the errata documentation for the errata.
-
Location: Specifies the location of the policy in the folder hierarchy. To change the location, click Select to specify the location for the policy in the folder hierarchy. The Select Location window appears. Select a folder in the Library to specify the location of the policy and then click Select.
-
Created: Corresponds to the time when the errata was downloaded by SA to create the software policy.
-
Last Modified: Corresponds to the time when the errata based policy was modified.
-
Availability: Contains the SA server life cycle values for the errata based software policy. The default value for an errata-based policy is set to Available.
-
Platform: Specifies the operating systems applicable to the errata. You can expand the list to see the selected platforms.
-
-
To save the changes, select Save from the File menu.
Errata caching
When importing errata, theSA SUSE Import tools keep track of the imported errata. Details of each imported erratum are stored in a cache file and subsequent runs will skip the cached errata completely. This improves performance as it avoids calls to SUSE and to SA Library. In the absence of cached data, these calls are being made even for errata that has not been modified and is up-to-date in the SA Library. Errata that has been modified by SUSE is updated anyway so there is no danger of having outdated errata after import.
A cache file is created for each channel (SUSE Manager Importer) and content label (SMT Importer).
The cache files are kept in the /var/opt/opsware/sles_import folder on the SA core server.The file name uses the prev_import_ch_<label>.dat pattern, where <label> is the SUSE Manager Importer channel label or the SMT content label.
Here are some sample file names:
-
prev_import_ch_SLES12-SP1-Updates:sle-12-x86_64.dat
-
prev_import_ch_sles12-pool-x86_64 .dat
As a result of the caching mechanism described above, the following scenarios are possible:
- An erratum is imported into the SA Library and then it is removed, renamed, or moved to another folder. When
suse_manager_importandsmt_importare run the next time, the erratum will not be re-imported into the SA Library. This is because the erratum details are present in the cache file, so it is skipped during the import. - The errata roll-up policy is created and then it is removed, renamed, or moved to another folder (for example, by using the SA Client). When
suse_manager_importorsmt_importare run the next time, the errata roll-up policy will be recreated but it will contain only the errata that has been previously published by SUSE.
We welcome your comments!
To open the configured email client on this computer, open an email window.
Otherwise, copy the information below to a web mail client, and send this email to hpe_sa_docs@hpe.com.
Help Topic ID:
Product:
Topic Title:
Feedback: