Searching the Help
To search for information in the Help, type a word or phrase in the Search box. When you enter a group of words, OR is inferred. You can use Boolean operators to refine your search.
Results returned are case insensitive. However, results ranking takes case into account and assigns higher scores to case matches. Therefore, a search for "cats" followed by a search for "Cats" would return the same number of Help topics, but the order in which the topics are listed would be different.
| Search for | Example | Results |
|---|---|---|
| A single word | cat
|
Topics that contain the word "cat". You will also find its grammatical variations, such as "cats". |
|
A phrase. You can specify that the search results contain a specific phrase. |
"cat food" (quotation marks) |
Topics that contain the literal phrase "cat food" and all its grammatical variations. Without the quotation marks, the query is equivalent to specifying an OR operator, which finds topics with one of the individual words instead of the phrase. |
| Search for | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Two or more words in the same topic |
|
|
| Either word in a topic |
|
|
| Topics that do not contain a specific word or phrase |
|
|
| Topics that contain one string and do not contain another | ^ (caret) |
cat ^ mouse
|
| A combination of search types | ( ) parentheses |
|
- Integrate
- Service Manager integration methods and tools
- HPE Change Configuration and Release Management (CCRM)
- SAP Solution Manager
- HPE Project and Portfolio Management Center (PPM)
- HPE Application Lifecycle Management/Quality Center (ALM/QC)
- HPE Release Control (RC)
- HPE Universal CMDB (UCMDB)
- HPE Operations Orchestration (OO)
- HPE Business Service Management (BSM)
- HPE Operations Manager i (OMi)
- Computer Telephony Integration (CTI) with the Web client
- Case Exchange framework
OMi - Service Manager integration overview
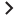
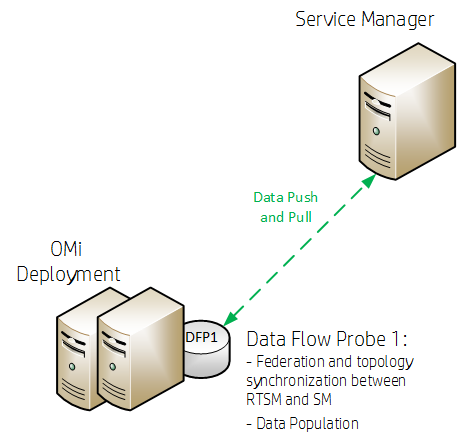
There are two variations of integrating Service Manager (SM) with OMi. One case uses the RTSM contained in OMi as the CMDB, and needs only one data flow probe (DFP1), which is installed in the OMi deployment. The other case uses a UCMDB, and needs two data flow probes (DFP1 installed on the UCMDB server and DFP2 in the OMi deployment).
Point to point integration
OMi is integrated with Service Manager directly, using OMi's Run Time Service Model (RTSM) as CMDB, as shown in the following figure.
HPE recommends installing the Data Flow Probe 1 (DFP1) in the OMi deployment.
Integration using a Universal Configuration Management Database (UCMDB)
OMi is set up using an external UCMDB, as shown in the following figure.
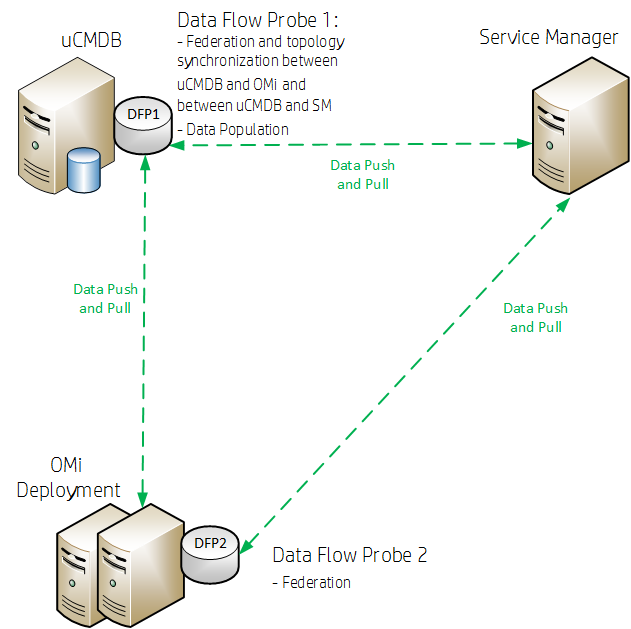
HPE recommends to install the Data Flow Probe 1 (DFP1) on the UCMDB server and the Data Flow Probe 2 (DFP2) in the OMi deployment.
Data flow probes
Two different data flow probes need to be installed. They have different purposes.
- DFP1 is needed for the following:
Populating the RTSM with CIs (Data Population)
Federation
Topology synchronization (CIs) between RTSM and SM in the case of a point to point integration
OR
Topology synchronization (CIs) between UCMDB and OMi and between UCMDB and SM in case of using an external UCMDB
- DFP2 is needed for federation only.
Prerequisites
If you are using a standalone CMDB, you need to do the following before continuing with the OMi- SM integration:
-
Set up the integration between OMi and UCMDB.
-
Integrate UCMDB with SM to synchronize CIs from UCMDB to SM.
For details, see Universal CMDB Integration Guide.
Integration options
-
Incident exchange between SM and OMi. OMi enables you to forward events from OMi to SM. Forwarded events and subsequent event changes are synchronized back from SM to OMi. You can also drill down from OMi events to SM incidents. For details, see Incident Exchange (OMi - SM) integration.
-
Downtime exchange between OMi and SM. OMi enables you to forward downtimes (also known as outages) from OMi to SM, and from SM to OMi. The downtime defined in OMi is directed to SM as an incident, and vice versa. For details, see Downtime Exchange between OMi and Service Manager.
-
View planned changes and incident details in Service Health. This integration enables you to view planned changes and incident details in the Changes and Incidents tab in the 360° View page in Service Health. For details, see the OMi Integration Guide.
-
The Business Impact Report integration is part of the Closed Loop Incident Process (CLIP) solution. When deployed as part of the OMi solution, Incident Management users can launch an impact report from an incident in context with the incident's affected CI. Service desk agents can validate the updated status of the business impact to categorize and prioritize the incident accordingly.
For details, see the CLIP page in the Solutions Portal and BSM Business Impact Report (BIR).
Note
-
Service Manager Query Security: If you have set up an integration from OMi to SM, there is a CI context menu that enables you to access SM from OMi Service Health. This drill-down option is not available if you have enabled Service Manager query security.
-
Troubleshooting Multiple Domains: If OMi and SM are in different domains, and you are using Internet Explorer as your browser, you may need to add the domains to the list of allowed domains in the Privacy tab (Internet Options > Privacy > Sites).
We welcome your comments!
To open the configured email client on this computer, open an email window.
Otherwise, copy the information below to a web mail client, and send this email to ovdoc-ITSM@hpe.com.
Help Topic ID:
Product:
Topic Title:
Feedback: