Searching the Help
To search for information in the Help, type a word or phrase in the Search box. When you enter a group of words, OR is inferred. You can use Boolean operators to refine your search.
Results returned are case insensitive. However, results ranking takes case into account and assigns higher scores to case matches. Therefore, a search for "cats" followed by a search for "Cats" would return the same number of Help topics, but the order in which the topics are listed would be different.
| Search for | Example | Results |
|---|---|---|
| A single word | cat
|
Topics that contain the word "cat". You will also find its grammatical variations, such as "cats". |
|
A phrase. You can specify that the search results contain a specific phrase. |
"cat food" (quotation marks) |
Topics that contain the literal phrase "cat food" and all its grammatical variations. Without the quotation marks, the query is equivalent to specifying an OR operator, which finds topics with one of the individual words instead of the phrase. |
| Search for | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Two or more words in the same topic |
|
|
| Either word in a topic |
|
|
| Topics that do not contain a specific word or phrase |
|
|
| Topics that contain one string and do not contain another | ^ (caret) |
cat ^ mouse
|
| A combination of search types | ( ) parentheses |
|
Identity Management
Concepts
Service Portal Identity Management (IdM) uses role-based access control, which controls whether a user can perform an operation based on the user's assignment to a role and the role's association with application-defined permissions.
The relationships among organizations, groups, roles, and permissions in Service Portal are:
- Permissions are the most basic unit of authorization. They enable access to Service Portal applications and services.
- Roles are user-defined collections of permissions. Roles are associated with groups that contain members (users).
- Groups have one or more users. A group can be associated with one or more roles, and a group belongs to one or more organizations.
- Organizations can contain one or more groups.
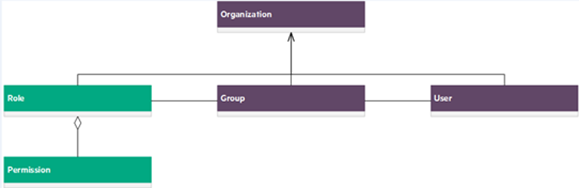
An organization determines a user's Service Portal entry point at log in and associates its group members with services and resources. Examples of organizations are companies, business units, and departments.
The Service Portal Administrator configures an LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) directory service to determine membership in a Service Portal organization.
When a user logs in, LDAP authenticates the login credentials by verifying that the user name and password match an existing user in the LDAP directory.
Authorization and abilities of an organization's user are determined by predefined roles and permissions and membership to group DNs (distinguished names) in the LDAP directory. You assign a group DN to a predefined role that has predefined abilities.
Tasks
The Administrator can perform the following tasks in the Identity application:
- Manage Organizations – Create, revise, and delete organizations.
- Manage Languages – Add, set as default, and delete languages within a Consumer organization.
- Manage Roles – Create, revise, and delete roles within an organization. You can also associate permissions to roles and remove associated permissions from roles.
- Manage Groups – Create, revise, and delete groups within an organization. You can also add users and roles to groups and remove users and roles from groups.
- Manage Permissions – Create, revise, and delete permissions within an organization. You can also associate groups and permissions to roles and remove groups and permissions from roles.
- Manage Impersonations – For request on behalf, create and delete impersonations.