Searching the Help
To search for information in the Help, type a word or phrase in the Search box. When you enter a group of words, OR is inferred. You can use Boolean operators to refine your search.
Results returned are case insensitive. However, results ranking takes case into account and assigns higher scores to case matches. Therefore, a search for "cats" followed by a search for "Cats" would return the same number of Help topics, but the order in which the topics are listed would be different.
| Search for | Example | Results |
|---|---|---|
| A single word | cat
|
Topics that contain the word "cat". You will also find its grammatical variations, such as "cats". |
|
A phrase. You can specify that the search results contain a specific phrase. |
"cat food" (quotation marks) |
Topics that contain the literal phrase "cat food" and all its grammatical variations. Without the quotation marks, the query is equivalent to specifying an OR operator, which finds topics with one of the individual words instead of the phrase. |
| Search for | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Two or more words in the same topic |
|
|
| Either word in a topic |
|
|
| Topics that do not contain a specific word or phrase |
|
|
| Topics that contain one string and do not contain another | ^ (caret) |
cat ^ mouse
|
| A combination of search types | ( ) parentheses |
|
Configure assignment rules for individuals
You can configure assignment rules for individuals so that a record can be automatically assigned to a specific individual for processing. The assignment rules can be configured either by using the Assignment form or by using JavaScript.
You can configure the assignment rules so that a record can be automatically assigned to the following individuals:
- None: Do not assign to any individual
- A member of the assigned group: The member can be decided in a round robin manner or based on the workload of the group members
- Coordinator of the assigned group
- A specific assignee
Assign in a round robin manner
In the round robin manner, the system checks the latest assignment time of the members in a group, and then assigns the record to the member who has the earliest assignment time.
If you have a huge number of records to be assigned in Service Manager, follow these guidelines to avoid possible performance issues:
- Only take recent assignments into account. By default, the value of 60 days is set while you add assignment rules in the round robin manner. You can adjust the value based on your needs. If this value is set to 60 days, it means that only assignments within the most recent 60 days are considered; assignments before 60 days are ignored. If the value is set to 0, it means there is no assignment time restriction; all the assignments of the members are considered.
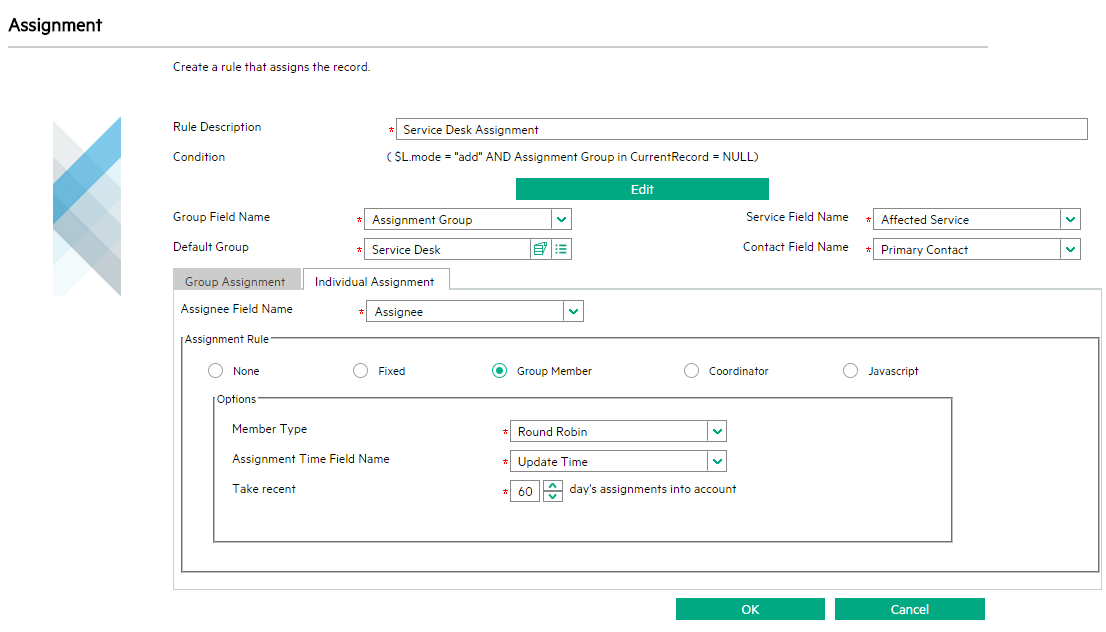
- Create index on the assignment time field and the assignee field of the corresponding table. This can avoid full table scans and thus can increase the query speed. At run time, the calculation SQL is as follows:
select [assignee field], max([assign time field]) time from [ticket file] where [assign time field] >= [assigned time restriction] and [assignee field] isin [members in group] group by [assignee field] order by time
Assign based on workload
You can use the "Number of Assigned Records" member type to configure the assignment rules so that a record can be assigned based on people's workload. The system checks the number of working records of all the members in a group and then assigns the record to the member who has least working records.
To avoid possible performance issues for this assignment type, follow these guidelines:
- Only take open records into account. Usually you need to append the query that filters out records other than the open records. You can use the Query Editor to edit the query string. In the example below, the query string Status != "Closed" is appended.
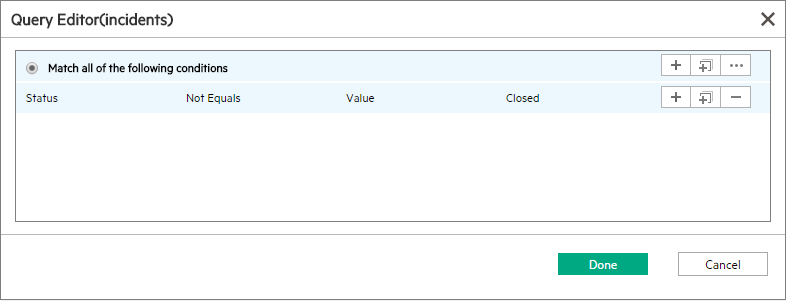
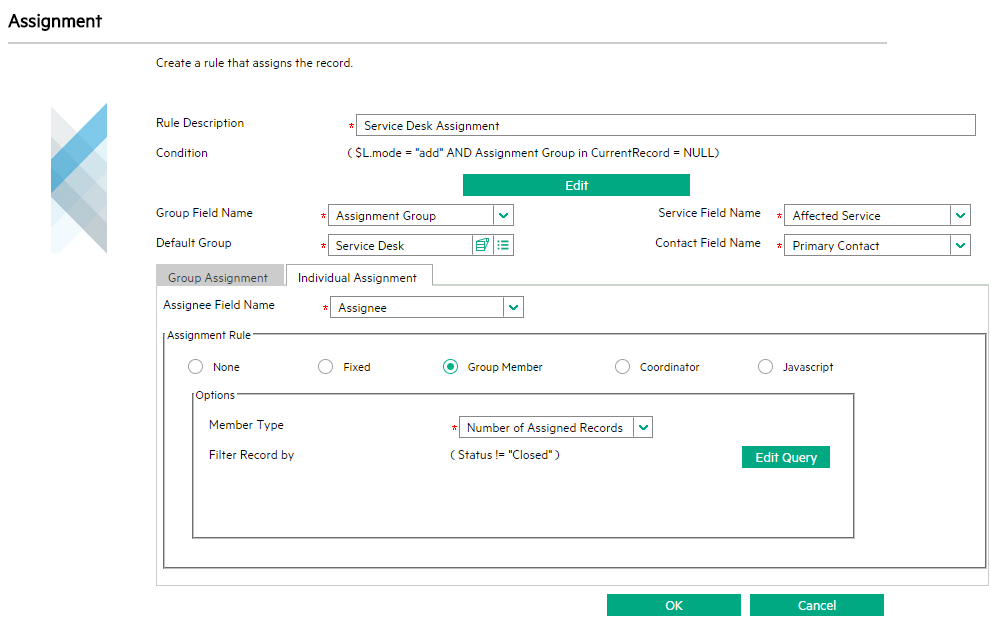
In addition, you can further narrow down the filter result. For example, if you plan to take only the open and critical records into account, you can append to the query string as shown below: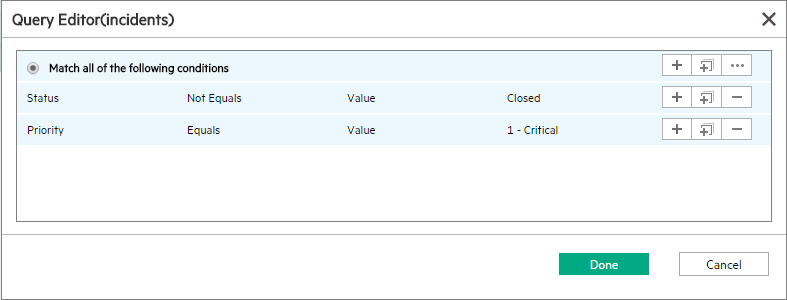
- Create index on the assignee field and the fields of the appended query. This can avoid full table scans and can thus increase the query speed. At run time, the calculation SQL is as follows:
select [assignee field], count(*) ncnt from [ticket file] where [assignee field] isin [members in group] and [the appended query string] group by [assignee field] order by ncnt
Use Javascript to configure assignment rules for individuals
In addition to using the configuration forms to configure assignment rules for individuals, you have the flexibility to use JavaScript to implement your assignment rules. In JavaScript, you can use the assigneeValue variable to specify an assignee.