Searching the Help
To search for information in the Help, type a word or phrase in the Search box. When you enter a group of words, OR is inferred. You can use Boolean operators to refine your search.
Results returned are case insensitive. However, results ranking takes case into account and assigns higher scores to case matches. Therefore, a search for "cats" followed by a search for "Cats" would return the same number of Help topics, but the order in which the topics are listed would be different.
| Search for | Example | Results |
|---|---|---|
| A single word | cat
|
Topics that contain the word "cat". You will also find its grammatical variations, such as "cats". |
|
A phrase. You can specify that the search results contain a specific phrase. |
"cat food" (quotation marks) |
Topics that contain the literal phrase "cat food" and all its grammatical variations. Without the quotation marks, the query is equivalent to specifying an OR operator, which finds topics with one of the individual words instead of the phrase. |
| Search for | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Two or more words in the same topic |
|
|
| Either word in a topic |
|
|
| Topics that do not contain a specific word or phrase |
|
|
| Topics that contain one string and do not contain another | ^ (caret) |
cat ^ mouse
|
| A combination of search types | ( ) parentheses |
|
APX permissions
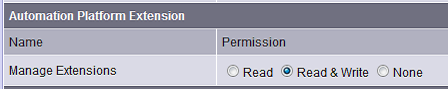
APXs requires that you have the SA Client Feature permission Manage Extensions. A user group can be given one of the permissions:
- Manage Extensions: Read
- Manage Extensions: Read & Write
- Manage Extensions: None
APX feature permissions
These feature permissions apply only to APX developers and administrators, they do not apply to those users who only need to run APXs.
- Read permission grants the ability to display the APX source contents or to export (download) the APX source archives.
- Read & Write permission grants the ability to modify the contents of an APX in addition to read access.
- None permission denies all access to the APX source.
In addition to the SA Client Feature Manage Extensions permission, folder permissions (list, read, write, execute) must be used to determine which APXs a user has access to.
|
Permission |
Description |
|---|---|
|
List |
Permission to list the system’s APXs. |
|
Read |
Permission to view APX contents. |
|
Write |
Permission to modify APX content and to import and export APXs. |
|
Execute |
Permission to run APXs and view APX properties. |
The following table shows a matrix of how permissions are determined based on the combination of the Manage Extensions feature permissions and folder permissions.
|
Folder Permission: |
Manage Extensions Permission: |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Read |
Read & Write |
None |
|
|
List |
List APXs |
List APXs |
List APXs |
|
Read |
Export APXs |
Export APXs |
List APXs |
|
Write |
Export APXs |
Import, export APXs |
List APXs |
|
Execute |
Run APXs |
Run APXs |
Run APXs |
Like other SA features, you can grant a user access to an APX and specify to which managed servers and/or policies the user can apply the APX.
If a user attempts to access a Web APX for which he does not have execution permission, the Web browser will receive an HTTP 403 Forbidden return code.
For more information on SA permissions, see the Server Automation Administration Guide on the HPE SSO portal.
Permission escalation
When executing an APX, the user has only the privileges to access resources and operations granted in SA. However, in some cases, it will be necessary to temporarily grant the user escalated permissions, privileges beyond the SA privileges, while executing an APX. You can explicitly grant certain privileges to users, over-and-above their default SA privileges, on a temporary basis while running an APX. Permission escalation is transparent to the user running the APX.
For example, you may want a user to be able to run a BIOS information gathering application on a managed server, but the user does not have the permissions granted to do so. You can write an APX for a user without the privileges required to run the BIOS gathering application that temporarily grants that user the required privileges. The user’s privileges return to the default after the APX ends its run.
Privilege escalation is specified in the file apx.perm file. For more information, see The APX permissions escalation configuration file - apx.perm.
We welcome your comments!
To open the configured email client on this computer, open an email window.
Otherwise, copy the information below to a web mail client, and send this email to hpe_sa_docs@hpe.com.
Help Topic ID:
Product:
Topic Title:
Feedback: