Searching the Help
To search for information in the Help, type a word or phrase in the Search box. When you enter a group of words, OR is inferred. You can use Boolean operators to refine your search.
Results returned are case insensitive. However, results ranking takes case into account and assigns higher scores to case matches. Therefore, a search for "cats" followed by a search for "Cats" would return the same number of Help topics, but the order in which the topics are listed would be different.
| Search for | Example | Results |
|---|---|---|
| A single word | cat
|
Topics that contain the word "cat". You will also find its grammatical variations, such as "cats". |
|
A phrase. You can specify that the search results contain a specific phrase. |
"cat food" (quotation marks) |
Topics that contain the literal phrase "cat food" and all its grammatical variations. Without the quotation marks, the query is equivalent to specifying an OR operator, which finds topics with one of the individual words instead of the phrase. |
| Search for | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Two or more words in the same topic |
|
|
| Either word in a topic |
|
|
| Topics that do not contain a specific word or phrase |
|
|
| Topics that contain one string and do not contain another | ^ (caret) |
cat ^ mouse
|
| A combination of search types | ( ) parentheses |
|
Remediation Process
See "Remediating and Installing Software" in the SA 10.50 Administration Guide for information about the fundamentals of SA remediation.
To ensure patch compliance, Ubuntu Patch Management identifies vulnerable managed servers and simultaneously deploys packages to many servers when a remediation process is performed. The remediation process examines and applies an entire patch policy, including multiple policies, to the managed servers to which it is attached. A policy must be attached to a server or a group of servers before you can remediate the policy with that server or group.
Best Practice: Each time you review the latest Ubuntu package releases and subsequently update a patch policy by adding new packages to a policy, you should perform remediation. In these situations, a remediation process provides demand forecasting information. This allows you to determine how patch policy changes will impact servers to which this policy is attached.
If the remediation process discovers any applicable missing packages, these packages will be installed on the servers.
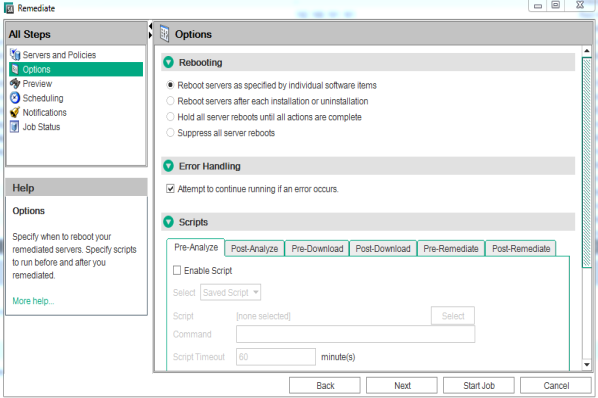
To help you manage remediation conditions, SA allows you to specify remediate options and pre and post actions, and set up ticket IDs and email notifications that alert you about the status of the remediate process. The Remediate wizard guides you through setting up these conditions.
Remediate Wizard
We welcome your comments!
To open the configured email client on this computer, open an email window.
Otherwise, copy the information below to a web mail client, and send this email to hpe_sa_docs@hpe.com.
Help Topic ID:
Product:
Topic Title:
Feedback: