Searching the Help
To search for information in the Help, type a word or phrase in the Search box. When you enter a group of words, OR is inferred. You can use Boolean operators to refine your search.
Results returned are case insensitive. However, results ranking takes case into account and assigns higher scores to case matches. Therefore, a search for "cats" followed by a search for "Cats" would return the same number of Help topics, but the order in which the topics are listed would be different.
| Search for | Example | Results |
|---|---|---|
| A single word | cat
|
Topics that contain the word "cat". You will also find its grammatical variations, such as "cats". |
|
A phrase. You can specify that the search results contain a specific phrase. |
"cat food" (quotation marks) |
Topics that contain the literal phrase "cat food" and all its grammatical variations. Without the quotation marks, the query is equivalent to specifying an OR operator, which finds topics with one of the individual words instead of the phrase. |
| Search for | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Two or more words in the same topic |
|
|
| Either word in a topic |
|
|
| Topics that do not contain a specific word or phrase |
|
|
| Topics that contain one string and do not contain another | ^ (caret) |
cat ^ mouse
|
| A combination of search types | ( ) parentheses |
|
Symbols Used in Maps
SAV uses a variety of symbols in the Network Map, Server Map, and Tiers Map, such as lines, arrows, diamonds, and so on. This section explains SAV map symbols in the following topics:
- Process and Links Connection Symbols
- Map Process and Network Connection Symbols
- Exporting a View to .png, .png, or .svg
- Printing a Map
- Showing IPC Service Names in Maps
Process and Links Connection Symbols
In the SAV maps, lines and arrows represent connections between process families. In some cases, SAV knows both the source of the connection and the destination. In other cases, SAV may only know either the source or the destination of the connection.
To represent these process connection relationships, SAV uses the following lines and arrows:
- Source Unknown — Diamond:
 An arrow with a diamond at its source indicates that SAV does not know the source of the connection. If there is a solid line from a process connection source (in other words, it doesn’t show a diamond) then SAV knows the connection source.
An arrow with a diamond at its source indicates that SAV does not know the source of the connection. If there is a solid line from a process connection source (in other words, it doesn’t show a diamond) then SAV knows the connection source. - Destination Unknown — Hollow Arrow:
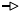 A hollow arrow represents an inbound connection to a process family destination that is unknown.
A hollow arrow represents an inbound connection to a process family destination that is unknown. - From Remote IP — Solid Arrow:
 A solid arrow represents an inbound client connection from a remote IP, such as TCP or UDP, where the destination process family is known.
A solid arrow represents an inbound client connection from a remote IP, such as TCP or UDP, where the destination process family is known. - From Process — Lined Arrow: A lined arrow represents a connection from a process family where the destination process family is known.
Map Process and Network Connection Symbols
In the SAV maps, lines represent the following connections between devices:
- Client link: An internal connection that is labeled by the client IP address.
- Process link: A collection of TCP or UDP connections between process families. This link displays processes that provide a network service, such as listening for network connections, and processes that have a connection to another process or server.
- Layer 1 connection: A physical link between a server’s network interfaces and switch ports/switches. Layer 1 connections are indicated by colored, dashed lines in the map: These connection symbols are also used for virtual server and device connections as well.
 A green dashed line indicates that there is no duplex mismatch.
A green dashed line indicates that there is no duplex mismatch. A red dashed line indicates that there is a duplex mismatch.
A red dashed line indicates that there is a duplex mismatch. A gray dashed line indicates that there may or may not be a duplex mismatch because at least one value is unknown.
A gray dashed line indicates that there may or may not be a duplex mismatch because at least one value is unknown. - Line Thickness: The thinness or thickness of the line represents the number of connections associated with the link. A smaller number is indicated by a thinner line and a larger number is indicated by a thicker line, as illustrated below.
Exporting a View to .png, .png, or .svg
--You can export a view to a .png, .png, or .svg file for use in other applications where you can annotate the drawing or map the exported file in a web browser.
To export a map to an image file:
- From the View menu, select Export View. (Or, click the Export View
 button at the upper right corner of the map.)
button at the upper right corner of the map.) - Select a directory where you want the file to be located.
- Enter a file name that includes either .png, .png, or .svg as the file name extension.
- Click Export View.
For information about exporting Properties to a .csv file, see Exporting properties information to .csv.
Printing a Map
You can print a map on single and multiple sheets of paper, and you can also title the map for better presentation.
If the map you want to print is very dense and complex, you can make adjustments by zooming in and zooming out, and by creating rows and columns that will break the map up over several pages. Doing this enables you to print the map on multiple sheets of paper, thus increasing the map’s readability.
To adjust the map before you print:
- Click Zoom In
 or Zoom Out
or Zoom Out  to increase or decrease the size of the map before you print.
to increase or decrease the size of the map before you print. - Enter a title for the map
To print a map, perform the following steps:
- From the File menu, select Print or select the
 toolbar icon.
toolbar icon. - (Optional) In the Print window, specify page setup and printer options, including a title that you want to appear on the printed map.
- Click Print.
Showing IPC Service Names in Maps
If you want to see the type of service being used for connections between processes (and the devices they run on) in the Network or Server map, such as http, ssh, click the Show IPC Service Names in Maps  on the SAV toolbar. The service name will appear on each connection line.
on the SAV toolbar. The service name will appear on each connection line.
To show IPC service names in the Server or Network map:
- Inside of SAV, select either the Server or Network map.
- From the View menu, select Show IPC Service Names in Maps.
Or, click Show IPC Service Names in Maps on the SAV toolbar
on the SAV toolbar
We welcome your comments!
To open the configured email client on this computer, open an email window.
Otherwise, copy the information below to a web mail client, and send this email to hpe_sa_docs@hpe.com.
Help Topic ID:
Product:
Topic Title:
Feedback: