Searching the Help
To search for information in the Help, type a word or phrase in the Search box. When you enter a group of words, OR is inferred. You can use Boolean operators to refine your search.
Results returned are case insensitive. However, results ranking takes case into account and assigns higher scores to case matches. Therefore, a search for "cats" followed by a search for "Cats" would return the same number of Help topics, but the order in which the topics are listed would be different.
| Search for | Example | Results |
|---|---|---|
| A single word | cat
|
Topics that contain the word "cat". You will also find its grammatical variations, such as "cats". |
|
A phrase. You can specify that the search results contain a specific phrase. |
"cat food" (quotation marks) |
Topics that contain the literal phrase "cat food" and all its grammatical variations. Without the quotation marks, the query is equivalent to specifying an OR operator, which finds topics with one of the individual words instead of the phrase. |
| Search for | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Two or more words in the same topic |
|
|
| Either word in a topic |
|
|
| Topics that do not contain a specific word or phrase |
|
|
| Topics that contain one string and do not contain another | ^ (caret) |
cat ^ mouse
|
| A combination of search types | ( ) parentheses |
|
- Inventory Discovery
- Inventory Discovery Overview
- Inventory Discovery Scanners
- Inventory Discovery Deployment Overview
- Scan Files
- Processing Scan Files
- Scan File Processing Power
- XML Enricher
- XML Enricher Log Files
- Application Teaching
- Using Rules to Teach Applications
- Enriched Scan File Structure
- Hardware and Software Recognition
- App Store Applications
- Custom Hardware or Asset Mapping
- Inventory Tools
- BDNA Normalize Integration
- Discovery Options for Client IP Ranges
- How to Run Inventory Discovery
- How to Run Inventory Discovery Manually
- How to View Discovery Status of an Inventory CI in JMX
- How to View Agent Deployment Log for an Inventory CI in JMX
- How to Edit Pre and Post Scan Scripts
- How to Set Up Asset Fields for Data Collection
- How to Set Up Asset Fields for Data Collection - Example
- How to Set up the Scanner to Handle Delta Scan Files in Manual Deployment Mode
- How to Configure XML Enricher to Suit the Probe Deployment Mode
- How to Configure the Maximum Number of Threads to Process Scan Files
- How to Check XML Enricher Health Using JMX
- How to Limit the XML Enricher Port to Allow Local Connection Only
- How to Reprocess Scan Files
- How to Import SAIs to the Data Flow Probe
- How to Import Normalization Rules to the Data Flow Probe
- How to Configure and Optimize Inventory Discovery
- How to Configure Analysis Asset Fields
- How to Map Scan File Attributes to UCMDB
- Mapping Hardware or Asset Fields to UCMDB - Use-Case Scenario
- How to Set Extract Options
- How to Filter Discovery Results to UCMDB
- How to Enable Application Virtualization Discovery
- How to Rename Scanner Executable Files
- How to Integrate BDNA Normalize
- How to Discover Client IP Ranges Without SNMP
- How to Discover Windows Device Drivers using the Inventory Discovery by Scanner Job
- Scanner Command Line Parameters Overview
- Scanner Command Line Parameters
- Scanner Information Type Parameters
- Scanner File Locations
- Web Server Configuration for Saving Scan Files via HTTP
- XML Enricher Directory Structure
- Enriched XSF File Structure
- Inventory Discovery User Interface
Inventory Discovery Scanners
After defining requirements, the next step in an IT asset inventory is to collect data. The data is collected by Scanners.
You configure and generate scanners using the Scanner Generator. Scanners are configured according to the specifications determined in the planning stage of the inventory.
The Scanner Generator is used to both configure and define the level of information to be collected. One or more scanner executable programs with the desired configuration are then generated and subsequently run across a computer population.
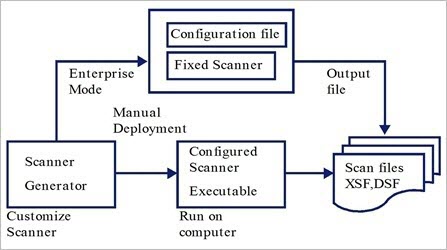
The Scanner Generator also provides a set of options for controlling the behavior of the scanner as it scans each computer, under both normal and exceptional conditions (such as when an error occurs).
Scanner Modes
The scanner is run across the computer population to collect inventory data in one of the following ways:
-
Enterprise Mode (default). Automatically collects an inventory using the Universal Discovery's scheduling and launching capabilities.
-
Manual Deployment Mode. Scans are launched manually. For example,scans are schedule and launched from login scripts or on non-networked machines.
Components of a Scanner
A scanner consists of the following files:
| The scanner executable file |
This file is an executable file. It contains the constant parts of the scanner:
|
| The scanner configuration file |
The configuration file is a compressed XML file containing the settings for the scanner you are currently configuring. When the scanners are used in Enterprise Mode, they read the configuration from a separate configuration file. This is a binary file with a .cxz extension. The typical size of the configuration file is about 3K. As the size of the configuration file is significantly smaller than the size of the complete scanner, a separate scanner configuration is useful for repetitive inventory collection when the configuration of the scanner has been altered. In this case, only a small configuration file is delivered to the user’s computer to run with the original scanner instead of delivering the entire new scanner. |
Note When used in Manual Deployment Mode, the Scanner Generator generates self-contained scanner executables that consist of a combination of the scanner executable and configuration file.
What Information Does the Scanner Collect?
Scanners can collect several types of information and can be configured to collect any or all of them. The details recorded for each computer within each main category depend on the options and settings selected when the scanner is generated and the configuration of the computer.
Scanners can collect the following information:
| Information | Description |
|---|---|
| Hardware and Configuration Information |
Hardware information is detected automatically. The scanners collect and store from 100 to 900 hardware items for a computer, depending on the type and manageability options available on the computer. The Scanner Generator allows a subset of the hardware collection to be disabled. Normally this is not required, but it may be desirable to decrease the scan file size or scan time. The hardware details that can be defined and recorded by the scanner include the following:
|
| Software Information | Software information is scanned automatically, and consists of detailed information about the files and directories on the drives scanned. The information collected about files can be defined (including the file types and the level of information collected). It is possible to define the drives that are to be scanned based on either the media or format of the drive, or to use the targeted scanning option to scan just a set of directories. Specific files can be collected (that is, stored in the scan file) for further analysis or for error recovery purposes. It is also possible to configure the level of file detail stored in the scan file and filters can be set up that specify directories or files to be included or excluded from being stored. |
| User or Asset Information | User or asset information consists of configurable fields that can be collected automatically. It usually includes the asset number which is used to uniquely identify each computer. Asset data fields are automatically populated from the data extracted from text files, the Windows registry/WMI and environment variables. |
| Software Utilization |
Universal Discovery can gather information about the software that is being used on the machines in your network. This is referred to as Software Utilization. The information collected can be used to optimize software license cost, for example by eliminating unused or under-utilized software installations. From a software recognition perspective, any files that are Unknown and are shown to have a high Utilization should be marked for teaching. Software utilization data shows the number of days that an application was used (as a percentage) over a period of time. This period of time is known as the Utilization Period. As a guideline the Utilization Periods are as follows:
|
We welcome your comments!
To open the configured email client on this computer, open an email window.
Otherwise, copy the information below to a web mail client, and send this email to cms-doc@microfocus.com.
Help Topic ID:
Product:
Topic Title:
Feedback: