Searching the Help
To search for information in the Help, type a word or phrase in the Search box. When you enter a group of words, OR is inferred. You can use Boolean operators to refine your search.
Results returned are case insensitive. However, results ranking takes case into account and assigns higher scores to case matches. Therefore, a search for "cats" followed by a search for "Cats" would return the same number of Help topics, but the order in which the topics are listed would be different.
| Search for | Example | Results |
|---|---|---|
| A single word | cat
|
Topics that contain the word "cat". You will also find its grammatical variations, such as "cats". |
|
A phrase. You can specify that the search results contain a specific phrase. |
"cat food" (quotation marks) |
Topics that contain the literal phrase "cat food" and all its grammatical variations. Without the quotation marks, the query is equivalent to specifying an OR operator, which finds topics with one of the individual words instead of the phrase. |
| Search for | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Two or more words in the same topic |
|
|
| Either word in a topic |
|
|
| Topics that do not contain a specific word or phrase |
|
|
| Topics that contain one string and do not contain another | ^ (caret) |
cat ^ mouse
|
| A combination of search types | ( ) parentheses |
|
- Change Management
- Change Management overview
- Change Management user roles
- Change Management workflows and user tasks
- Create a new change record
- Create a change request from a change proposal
- Create a new change with a Release Management category
- Apply a change model to an existing change record
- Update a change request
- Update multiple change requests
- Update multiple task records
- Return a change request to the requester
- Abandon a change request
- Assign a change owner for a change request
- Assess the risk and impact of a change
- Prioritize a change request
- Plan and schedule a Standard change
- Use Task Planner to plan change tasks
- Cancel open tasks for a change record
- Validate a Normal change
- Relate a change to another record
- Unrelate a change to another record
- Approve a change request
- Update an active approval delegation
- Delegate approvals to another operator
- Disable an active approval delegation
- Copy an approval delegation
- Build and test a change
- Implement a Standard change
- Implement an Emergency change
- Implement a Normal change
- Update the CMDB for associated configuration items
- Close a change task
- Review and close a change
- Reopen a change request or task
- View the alert log of a change
- Change the phase of a change
- Change the category of a change
- Print a change request
- Print a change request list
- Set a reminder for a change request
- View a list of services potentially affected by an outages
- Send a notification from a task or change request
- Manually calculate Time Period conflicts for a change
- Access Change Management reports
- Change Management administration
- Change Management configuration
- Security
Change Management workflows and user tasks
Change Management controls the process to request, manage, approve, and control changes that modify your organization’s infrastructure. This managed infrastructure includes assets such as, network environments, facilities, telephony, and resources. For user requests for products and services, refer to Request Fulfillment overview.
Change Management automates the approval process and eliminates the need for memos, E-mail, and phone calls, based on the following workflows.
Note The Standard, Normal, and Emergency change workflows have an implementation phase, which is named Execution, Deployment, or Implementation, respectively. The names are by design and selected to match the types of activities for the flows as specified in ITIL. The implementation phase in each workflow is named differently because the activities are different.
Change Proposal (ST 2.0)
Change proposals are submitted to change management before chartering new or changed services in order to ensure that potential conflicts for resources or other issues are identified. Authorization of the change proposal does not authorize implementation of the change but simply allows the service to be chartered so that the service design activities can commence.
A change proposal is used to communicate a high-level description of the change. This change proposal is normally created by the service portfolio management process and is passed to change management for authorization. In some organizations, change proposals may be created by a programme management office or by individual projects.
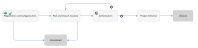
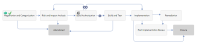
The following figure depicts the Change Proposal workflow in Process Designer.
The following table lists the user tasks during each phase of the workflow.
| Phase | Tasks |
|---|---|
| Registration and Categorization | |
| Risk and Impact Analysis | |
| Authorization | |
| Project Initiation | |
| Closure | |
| Abandoned |
Standard Change (ST 2.2)
A Standard Change is a pre-authorized change that follows a standard procedure, for example, a password reset or the provision of standard equipment to a new employee. Standard Change uses the Change Model configured in the system which can pre-populate the information in the change record on registering the Change.
For an activity to be accepted as a Standard Change, the following requirements must be met:
- The documented tasks must be commonly known and proven
- Authority will be given in advance based on predetermined criteria
- The chain of events can be initiated by a functional Service Desk
- Budgetary approval will typically be predetermined or within the control of the Change Requester
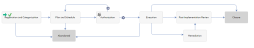
The following figure depicts the Standard Change workflow in Process Designer.
The following table lists the user tasks during each phase of the workflow.
| Phase | Tasks |
|---|---|
| Registration and Categorization | |
| Plan and Schedule | |
| Authorization | |
| Execution | |
| Abandoned | |
| Remediation | |
| Post Implementation Review | |
| Closure |
Normal Change (ST 2.3)
A Normal Change is a change that is categorized, prioritized, planned and that follows all approvals before deployment. The Normal Change activities describe the steps necessary to process a Normal Change by coordinating work effort. Normal Change can be further categorized as Major and Minor. Both Major and Minor changes go through the same workflow except that, for a Normal Major RFC the TCAB Approval phase is a manual transition & the change has to be approved manually by TCAB members. In a Normal Minor RFC the TCAB Approval phase is auto approved, this phase is optional in Minor RFC but it is still configured in Out of Box. The Change must be appropriately reviewed, approved, and executed successfully through the Normal Change process at least once prior to acceptance.
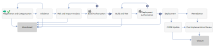
The following figure depicts the Normal Change workflow in Process Designer.
The following table lists the user tasks during each phase of the workflow.
| Phase | Tasks |
|---|---|
| Registration and Categorization | |
| Abandoned | |
| Validation | |
| Risk and Impact Analysis | |
| Build Authorization | |
| Build and Test | |
| Deployment Authorization | |
| Deployment | |
| Remediation | |
| CMDB Update | |
| Post Implementation Review | |
| Closure |
Emergency Change (ST 2.4)
An Emergency Change can also be initiated in the Incident Management process. They should be used only to repair an IT service error that is negatively impacting the business at a high level of severity. Changes that are intended to make an immediately required business improvement are handled as normal changes, although they may be assigned a high priority based on the urgency of the required business improvement.
The emergency change process follows the normal change process, except for the following:
- Approval is given by the Emergency Change Approval Board (E-CAB) instead of waiting for a regular CAB meeting.
- Testing may be reduced, or in extreme cases eliminated, if doing so is considered necessary to deliver the change immediately.
- Updating of the change request and configuration data may be deferred, till normal working hours.
If the E-CAB decides to handle an emergency change as a normal change, the emergency change is re-categorized and implemented using the Normal Change process.
The following user roles are involved in Emergency Change Handling:
- Change Manager
- E-CAB
- Change Owner
The following figure depicts the Emergency Change workflow in Process Designer.
The following table lists the user tasks during each phase of the workflow.
| Phase | Tasks |
|---|---|
| Registration and Categorization | |
| Risk and Impact Analysis | |
| Build Authorization | |
| Build and Test | |
| Abandoned | |
| Implementation | |
| Remediation | |
| Post Implementation Review | |
| Closure |
Related topics