Searching the Help
To search for information in the Help, type a word or phrase in the Search box. When you enter a group of words, OR is inferred. You can use Boolean operators to refine your search.
Results returned are case insensitive. However, results ranking takes case into account and assigns higher scores to case matches. Therefore, a search for "cats" followed by a search for "Cats" would return the same number of Help topics, but the order in which the topics are listed would be different.
| Search for | Example | Results |
|---|---|---|
| A single word | cat
|
Topics that contain the word "cat". You will also find its grammatical variations, such as "cats". |
|
A phrase. You can specify that the search results contain a specific phrase. |
"cat food" (quotation marks) |
Topics that contain the literal phrase "cat food" and all its grammatical variations. Without the quotation marks, the query is equivalent to specifying an OR operator, which finds topics with one of the individual words instead of the phrase. |
| Search for | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Two or more words in the same topic |
|
|
| Either word in a topic |
|
|
| Topics that do not contain a specific word or phrase |
|
|
| Topics that contain one string and do not contain another | ^ (caret) |
cat ^ mouse
|
| A combination of search types | ( ) parentheses |
|
- Install
- Deployment architecture
- Support matrix
- Recommended installation order
- Download the Service Manager installation packages
- Prepare your RDBMS
- Install the Service Manager Server
- Install the Service Manager web tier
- Install the Service Manager Windows Client
- Install language packs
- Install and set up Service Portal
- Install Service Request Catalog (SRC)
- Install the Mobile Applications client
- Install and configure Smart Analytics
- Install and configure the Solr Search Engine
- Install Service Manager Collaboration
- Set up a replicated reporting database
- Set up legacy integrations
- Install the Identity Manager (IdM) service
Deployment architecture
You can install Service Manager in a production environment or in non-production environments: development, test, and reporting environments. We recommend that you perform the installation in a development environment and then convert or push the installation to your production environment.
- Production environment: The production environment enables you to deploy your customizations and provide services to your user base. Most production environments run 24 hours a day and 7 days a week, support many simultaneous users, and process large numbers of transactions and requests. In a production environment, you typically install the components of Service Manager on dedicated servers to maximize system performance.
- Development environment: A development environment enables you to evaluate application features and customize your installation prior to deployment in a production environment. In a development environment, you typically install all Service Manager components on one test system with a limited number of users and data.
- Test environment: A test environment is an installation that mirrors your production environment where you can safely test performance, upgrades, and backup and restore procedures. In a test environment, you typically install Service Manager in the same configuration as your production environment.
- Reporting environment: A reporting environment is an installation that mirrors the data from your production environment that you use to generate and view reports. In a reporting environment, you typically install Service Manager to synchronize data with your production environment but limit the number of users that access the system.
Service Manager environment overview diagram
The Service Manager environment overview diagram describes the components of a Service Manager installation. The Service Manager table below provides a description for each component and lists whether the component is required or optional.
Note This diagram does not include the following Service Manager components: Solr Search Engine, Smart Analytics, Service Manager Collaboration, and Micro Focus Identity Manager (IdM). Refer to their specific installation sections for their deployment architectures.
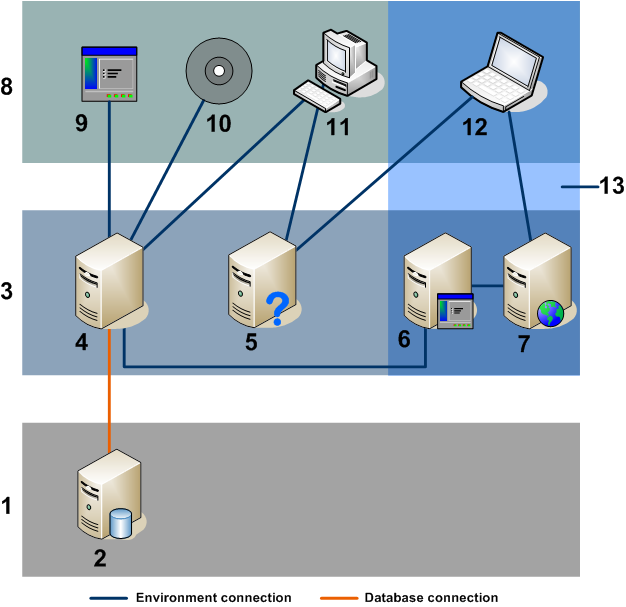
| Item | Name | Required? | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Database Tier | Required | Consists of one or more supported RDBMS servers. Your Service Manager application data must reside in an external RDBMS. |
| 2 | RDBMS | Required | A relational database management system for storing Service Manager applications and data. Requires a 1 GB network connection to the Service Manager Server. |
| 3 | Server Tier | Required | Contains servers that provide or process data for clients. The server tier includes the Service Manager server, which runs the Service Manager applications and manages the connections between the client and web tiers to the database tier. |
| 4 | Micro Focus Service Manager Server | Required | Manages connections between clients and the database tier. |
| 5 | Help Server | N/A |
This is the Micro Focus documentation server on which the Service Manager help center is published: docs.microfocus.com. |
| 6 | Web Applications Server | Optional | Offers Java applications and content for web clients. |
| 7 | Web Server | Optional | Provides HTTP or HTTPS content to web clients. |
| 8 | Client Tier | Required | Contains the applications and methods available for connecting to Service Manager. |
| 9 | Web Applications | Optional |
Applications that can connect to or communicate with Service Manager through a web services API. |
| 10 | Micro Focus Products | Optional |
The suite of applications that can connect to or communicate with the Service Manager server. Temporary licenses are integrated with the Service Manager server. For a complete and up-to-date list of Micro Focus integrations, see the Service Manager Compatibility Matrix on the Micro Focus Software Integration Portal. |
| 11 | Windows Client | Required | Intended for Service Manager administrators or implementers. The Windows Client must be installed on a Windows workstation and requires a separate installation on each system that you want to connect to Service Manager. Each installation consumes a license. You must install at least one Windows Client, depending on the number of administrators and power users. The Windows Client enables you to design forms and work with the dbdict, capabilities that are not available to the Web client user. Requires a 100 MB network connection to Service Manager (SOAP over HTTP or HTTPS). |
| 12 | Web Client | Optional |
Recommended for end users. A web client enables users to connect to the Service Manager server using a web browser, without needing to install any additional software on the user’s system. You can install a web client once and then any number of web users can access Service Manager from a single URL without consuming a license. Service Manager provides three end user portals: Employee Self-Service (ESS), Service Request Catalog (SRC), and Service Manager Service Portal. You can select one of them according to your needs. Note There are scaling issues to consider: one web application server can only handle so many concurrent users before you need additional servers to handle the load. |
| 13 | Web Tier | Optional |
Web application server and web server combinations that enable users to connect via a web browser. Third-party server software that provides the HTTP or HTTPS content to Service Manager web clients. Some web application servers also include built-in or bundled web servers. |
Components
A Service Manager installation may include the following components:
- Core components
- Server
Windows Client
Install at least one Windows Client for the system administrator or group of power users. The Windows Client provides some system administration functionalities that are not available from the Web Tier client.
Web Tier
The Web Tier client provides several views: Power User, Employee Self-Service (ESS), Accessible, and Self-Service Accessible.
- Database
- Applications
- Other components
Language Packs: A language pack is required when users need to use a localized version of Service Manager.
Smart Analytics or Solr Search Engine
To enable Knowledge Management search, install either of them. If you have purchased Smart Analytics, do not use the Solr Search Engine. Additionally, once Smart Analytics is enabled, you can no longer use the Solr Search Engine.
Service Request Catalog (SRC) or Service Manager Service Portal
SRC or Service Manager Service Portal can be used as a replacement for the ESS user portal. Both of them are a user portal through which users can submit support requests, order catalog items, search knowledge, and complete surveys.
Collaboration
Collaboration is an instant messaging solution combining IT Collaboration and End User Chat.
Micro Focus Identity Manager (IdM) service
The IdM service is required only if you want to enable SAML Single Sign-On for Service Manager.
JRE support
As of version 9.50, Service Manager (SM) adds the support of Open Java Development Kit (OpenJDK) for all SM components that require a JRE or JDK to work.
Important Out-of-box, an OpenJDK JRE is bundled with the Windows Server, Windows Client, and Service Manager Service Portal so that you do not have to manually install a JRE for them. For the other components, including the Linux Server installation package, you need to manually install either an OpenJDK JRE or Oracle JRE.
You have the option to use either Oracle JDK or OpenJDK with Service Manager. For the supported versions of Oracle JRE and OpenJDK JRE, see the Service Manager Support Matrix.
JRE bitness
For the Server (both Windows and Linux) and Windows Client: use 32-bit JRE.
For the rest of the components: use a JRE with the same bitness as the operating system.
How to use OpenJDK with Service Manager
Use OpenJDK with SM components as described in the following table.
Caution Service Manager does not support enabling FIPS mode with OpenJDK. If you want to enable FIPS mode for Service Manager, use Oracle or IBM JDK as needed.
| Component(s) | How to use OpenJDK |
|---|---|
|
An OpenJDK jre folder is already bundled with the components. No installation is required. |
| Linux Server |
Follow the steps for specific for your Linux operating system. Important For Red Hat Linux 7.1, the 32-bit OpenJDK cannot be installed by the yum command. You need to upgrade to version 7.2 or higher or use Oracle JDK instead.
|
|
Note If the web tier or Mobility Client is deployed on WebSphere, IBM JDK must be used instead.
|
| Solr Search Engine |
|
How to use Oracle JDK with Service Manager
Note Before you proceed, make sure that Oracle JDK or JRE is already installed on the corresponding system (SM Server, Windows Client, and so on).
Use Oracle JDK as described in the following table.
| Component | How to use Oracle JDK |
|---|---|
| Windows Server |
|
| Windows Client |
|
| Linux Server |
|
|
Web tier SRC Mobility Client |
Note If these components are deployed on WebSphere, you must use IBM JDK instead.
|
| Solr Search Engine |
|











