Searching the Help
To search for information in the Help, type a word or phrase in the Search box. When you enter a group of words, OR is inferred. You can use Boolean operators to refine your search.
Results returned are case insensitive. However, results ranking takes case into account and assigns higher scores to case matches. Therefore, a search for "cats" followed by a search for "Cats" would return the same number of Help topics, but the order in which the topics are listed would be different.
| Search for | Example | Results |
|---|---|---|
| A single word | cat
|
Topics that contain the word "cat". You will also find its grammatical variations, such as "cats". |
|
A phrase. You can specify that the search results contain a specific phrase. |
"cat food" (quotation marks) |
Topics that contain the literal phrase "cat food" and all its grammatical variations. Without the quotation marks, the query is equivalent to specifying an OR operator, which finds topics with one of the individual words instead of the phrase. |
| Search for | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Two or more words in the same topic |
|
|
| Either word in a topic |
|
|
| Topics that do not contain a specific word or phrase |
|
|
| Topics that contain one string and do not contain another | ^ (caret) |
cat ^ mouse
|
| A combination of search types | ( ) parentheses |
|
Configure Run Scheduled Action rules
You can configure the Run Scheduled Action rules to enable Service Manager to perform scheduled automatic operations on the current record. This rule can be used in situations like automatic record closure.
For example, you might want the system to automatically close the incidents that were resolved seven days ago. To do that, first define a rule set with the Run Scheduled Action rules. You can define the rule set on the table “probsummary” that stores incident records, as shown below:

In addition to the above configurations, you also need to configure the Run Scheduled Action rules in this rule set as follows:
- Set the conditions as follows. This only takes the low priority incidents into account.
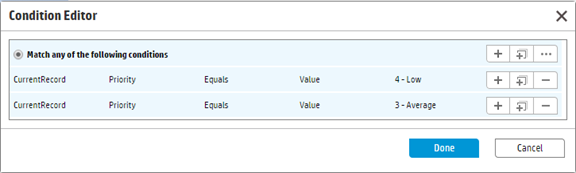
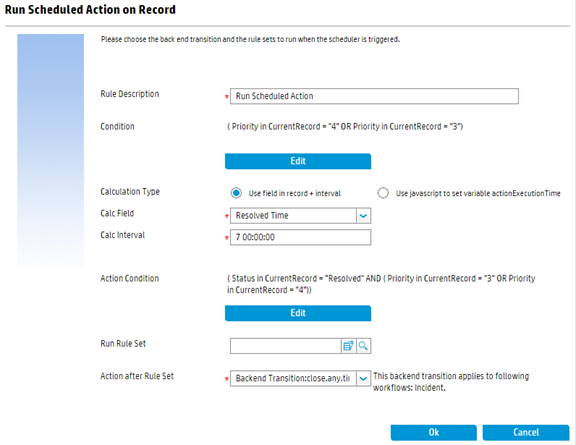
At run time, only when the condition is matched, this rule is executed to generate a scheduled record with the class of “scheduledAction”. Note that this rule type introduces a new back end scheduler process named “Scheduled Action processor”, which checks for the schedule records and executes them. - Select Use field in record + interval for the Calculation Type field
- Select Resolved Time for the Calc Field fieldNote: Make sure the resolve time of the incident is set correctly while the incident is resolved, because the schedule execution time is calculated based on the value of that field.
- Set 7 00:00:00 for the Calc Interval field. This means the scheduled action is executed after seven days.
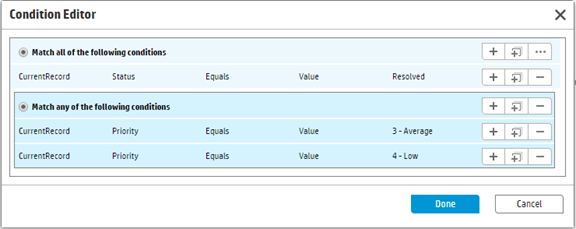
- Set the Action Condition as follows. The condition is checked when the scheduled time arrives. In this example, it is seven days after the incident is resolved. Only when the status of the incident is still Resolved, and the priority is still low at the time, the action is executed; otherwise the action is ignored.
- Keep the Run Rule Set field empty
- Select Backend Transition:close.any.time for the "Action after Rule Set" field. The save action is executed against the current record by the back end scheduler process when the scheduled time arrives.
- The back end transition list is retrieved from all the workflows of the selected record file. Similar to Configure Run Action rules on related records, at run time, if some of the other records do not have your selected back end transition, the corresponding transition is not run.
- You are suggested to use the same back end transition name in different workflows if these backend trasitions follow the same business logic.
- While a back end transition is selected from the list, the interface is updated to indicate to which workflows the transition applies and to which it does not apply.
The form on which you can perform these tasks is shown below:
To make the Run Scheduled Action rules work at run time, make sure the back end processor “Scheduled Action processor” is started, as shown below:












