Searching the Help
To search for information in the Help, type a word or phrase in the Search box. When you enter a group of words, OR is inferred. You can use Boolean operators to refine your search.
Results returned are case insensitive. However, results ranking takes case into account and assigns higher scores to case matches. Therefore, a search for "cats" followed by a search for "Cats" would return the same number of Help topics, but the order in which the topics are listed would be different.
| Search for | Example | Results |
|---|---|---|
| A single word | cat
|
Topics that contain the word "cat". You will also find its grammatical variations, such as "cats". |
|
A phrase. You can specify that the search results contain a specific phrase. |
"cat food" (quotation marks) |
Topics that contain the literal phrase "cat food" and all its grammatical variations. Without the quotation marks, the query is equivalent to specifying an OR operator, which finds topics with one of the individual words instead of the phrase. |
| Search for | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Two or more words in the same topic |
|
|
| Either word in a topic |
|
|
| Topics that do not contain a specific word or phrase |
|
|
| Topics that contain one string and do not contain another | ^ (caret) |
cat ^ mouse
|
| A combination of search types | ( ) parentheses |
|
Configure Run Action rules on other records
You can configure the Run Action rules to enable Service Manager to perform automatic operations on other records. The relationship of the records is built by manually defined query string. For example, you might want to sync up the status of an incident to its relevant incident tasks, that is to say, if the incident is suspended, the relevant incident tasks should be suspended as well.
To configure Run Action rules on other records, follow these steps:
- Define a rule set on the source table
- Define a rule set on the target table
- Configure the rule set on the source table into an appropriate workflow
Define a rule set on the source table
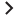
In this example, you can define the rule set on the source table “probsummary” that stores incident records:
In addition to the above configuration, you also need to configure the Run Action rules in the rule set as follows:
- Select Other Records for the "Run Action on" field.
- Select imTask for the "Table Name" field. This means the target records are incident tasks.
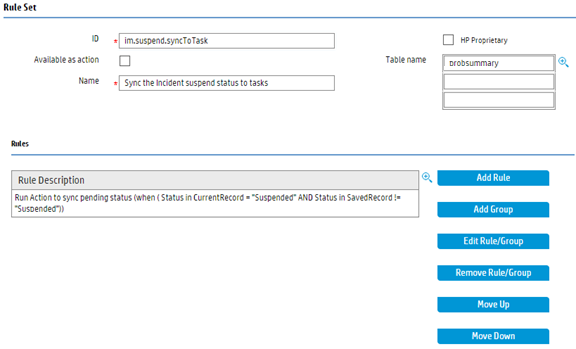
- Use the Query Editor to configure the Filter Record as shown below. The only incident task that belongs to current incident record is included.
- Select im.task.syncSuspendFromParent for the Run Rule Set field. This rule set is executed against the related incident task.
- Select Save for the "Action after Rule Set" field. The save action is executed against the related incident task.
- The back end transition list is retrieved from all the workflows of the selected record file. Similar to Configure Run Action rules on related records, at run time, if some of the other records do not have your selected back end transition, the corresponding transition is not run.
- You are suggested to use the same back end transition name in different workflows if these back end transitions follow the same business logic.
- While a back end transition is selected from the list, the interface is updated to indicate to which workflows the transition applies and to which it does not apply.
The form on which you can perform these tasks is shown below:

Define a rule set on the target table
You need to define a rule set on the target table. This rule set is used as the value of the "Run Rule Set" field when you define the rule set on the source table. In this example, you define the rule set “im.task.syncSuspendFromParent” on the target table “imTask” that stores the incident task records.

You need to configure a Set Field rule to change the status of the incident task to the value of “Suspended”. To do this, you can use JavaScript, in which you can refer to the current source record as srcRecord and the original copy of the source record (before any changes are made by the user) as oldSrcRecord. The system only supports invoking the current rule from the Run Action rule at run time.

In JavaScript, the current record and the original copy of the record are also referred as record and oldRecord. In this example, they are the current incident task record and original incident task record.
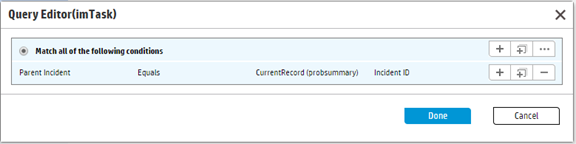
Configure the rule set on the source table into an appropriate workflow
In this example, you can configure the rule set into the After successful update event of the incident workflow, which means when the status of the incident record is changed to “Suspended”, the rule set is triggered.
We welcome your comments!
To open the configured email client on this computer, open an email window.
Otherwise, copy the information below to a web mail client, and send this email to ovdoc-ITSM@hpe.com.
Help Topic ID:
Product:
Topic Title:
Feedback: