Searching the Help
To search for information in the Help, type a word or phrase in the Search box. When you enter a group of words, OR is inferred. You can use Boolean operators to refine your search.
Results returned are case insensitive. However, results ranking takes case into account and assigns higher scores to case matches. Therefore, a search for "cats" followed by a search for "Cats" would return the same number of Help topics, but the order in which the topics are listed would be different.
| Search for | Example | Results |
|---|---|---|
| A single word | cat
|
Topics that contain the word "cat". You will also find its grammatical variations, such as "cats". |
|
A phrase. You can specify that the search results contain a specific phrase. |
"cat food" (quotation marks) |
Topics that contain the literal phrase "cat food" and all its grammatical variations. Without the quotation marks, the query is equivalent to specifying an OR operator, which finds topics with one of the individual words instead of the phrase. |
| Search for | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Two or more words in the same topic |
|
|
| Either word in a topic |
|
|
| Topics that do not contain a specific word or phrase |
|
|
| Topics that contain one string and do not contain another | ^ (caret) |
cat ^ mouse
|
| A combination of search types | ( ) parentheses |
|
Problem management process overview
The problem management process includes the activities that are required to identify and classify problems, diagnose the root cause of incidents, and determine resolutions to related problems. The process ensures that the resolution is implemented through the appropriate control processes, such as change management.
Problem Management includes the activities that are required to prevent the recurrence or replication of incidents. It enables you to form recommendations for improvement, maintain problems, and review the status of corrective actions.
Proactive problem management encompasses problem prevention, ranging from the prevention of individual incidents (for example, repeated difficulties with a particular system feature) to the formation of higher-level strategic decisions. The latter may require major expenditures to implement, such as investment in a better network. At this level, proactive problem management merges into availability management. Problem prevention also includes the information that is given to customers for future use. This information reduces future information requests and helps to prevent incidents caused by lack of user knowledge and training.
The following figure provides a general overview of the problem management processes and workflows. These workflows are described in detail in Problem Management Workflows.
Problem management phases
Service Manager uses phases to describe the steps needed to resolve a problem. The phase also determines the forms users see, the actions users can manually trigger. In an out-of-box system, most of the phase transitions are triggered by change to the problem status.
The following figure shows the workflow phases for a problem.
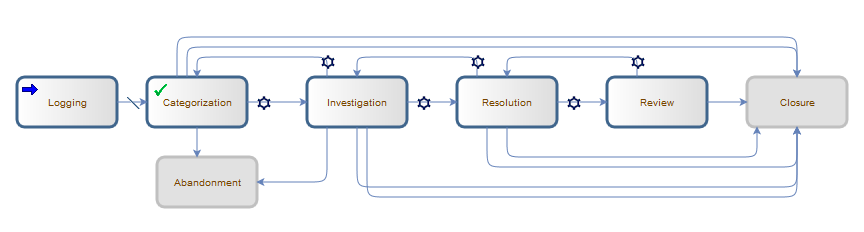
The out-of-box known error workflow uses only two phases to differentiate the open and closed known error records. A known error is opened with a documented root cause and workaround, and closed when a permanent solution is found.
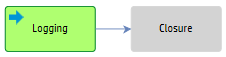
The following figure shows the workflow phases for a known error:
Problem Management user roles
The following table describes the responsibilities of the Problem Management user roles.












