Searching the Help
To search for information in the Help, type a word or phrase in the Search box. When you enter a group of words, OR is inferred. You can use Boolean operators to refine your search.
Results returned are case insensitive. However, results ranking takes case into account and assigns higher scores to case matches. Therefore, a search for "cats" followed by a search for "Cats" would return the same number of Help topics, but the order in which the topics are listed would be different.
| Search for | Example | Results |
|---|---|---|
| A single word | cat
|
Topics that contain the word "cat". You will also find its grammatical variations, such as "cats". |
|
A phrase. You can specify that the search results contain a specific phrase. |
"cat food" (quotation marks) |
Topics that contain the literal phrase "cat food" and all its grammatical variations. Without the quotation marks, the query is equivalent to specifying an OR operator, which finds topics with one of the individual words instead of the phrase. |
| Search for | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Two or more words in the same topic |
|
|
| Either word in a topic |
|
|
| Topics that do not contain a specific word or phrase |
|
|
| Topics that contain one string and do not contain another | ^ (caret) |
cat ^ mouse
|
| A combination of search types | ( ) parentheses |
|
- Hardening
This
This
A reverse proxy is an intermediate server that is positioned between the client machine and the web server(s). To the client machine, the reverse proxy seems like a standard web server that serves the client machine’s HTTP or HTTPS protocol requests with no dedicated client configuration required.
The client machine sends ordinary requests for web content, using the name of the reverse proxy instead of the name of a web server. The reverse proxy then sends the request to one of the web servers. Although the response is sent back to the client machine by the web server through the reverse proxy, it appears to the client machine as if it is being sent by the reverse proxy.
OMi supports a reverse proxy in DMZ architecture. The reverse proxy is an HTTP or HTTPS mediator between the OMi data collectors/application users and the OMi servers.
Reverse proxy configuration
The use of a reverse proxy is illustrated in the diagram below. Your data collectors may access OMi through the same virtual host or a different virtual host as your application users. For example, your environment may use one load balancer for application users and one load balancer for data collectors.
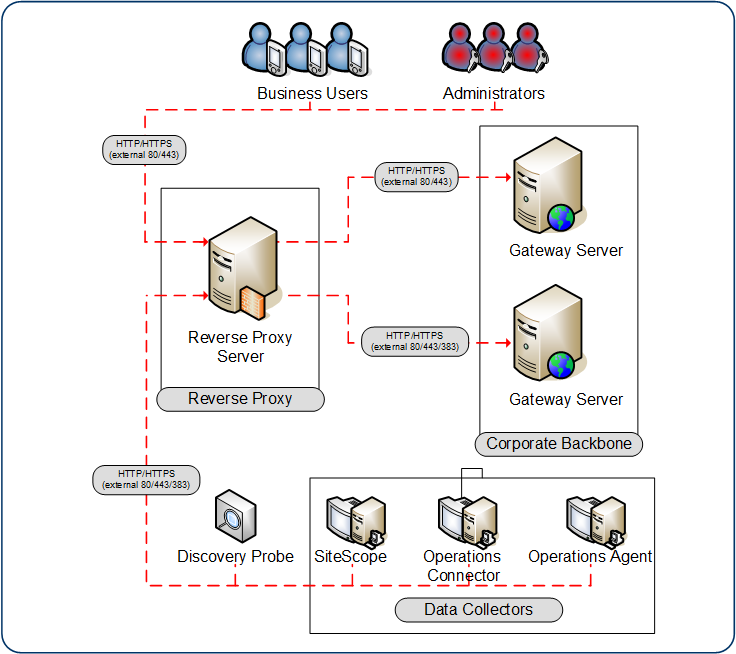
Reverse proxy OMi support should be configured differently in each of the following cases:
| Scenario # | OMi Components Behind the Reverse Proxy |
|---|---|
| 1 | Data collectors (SiteScope, Data Flow Probe, OpsCx, Operations Agent) |
| 2 | Application users |
| 3 | Data collectors and application users |
We welcome your comments!
To open the configured email client on this computer, open an email window.
Otherwise, copy the information below to a web mail client, and send this email to ovdoc-asm@hpe.com.
Help Topic ID:
Product:
Topic Title:
Feedback: