Searching the Help
To search for information in the Help, type a word or phrase in the Search box. When you enter a group of words, OR is inferred. You can use Boolean operators to refine your search.
Results returned are case insensitive. However, results ranking takes case into account and assigns higher scores to case matches. Therefore, a search for "cats" followed by a search for "Cats" would return the same number of Help topics, but the order in which the topics are listed would be different.
| Search for | Example | Results |
|---|---|---|
| A single word | cat
|
Topics that contain the word "cat". You will also find its grammatical variations, such as "cats". |
|
A phrase. You can specify that the search results contain a specific phrase. |
"cat food" (quotation marks) |
Topics that contain the literal phrase "cat food" and all its grammatical variations. Without the quotation marks, the query is equivalent to specifying an OR operator, which finds topics with one of the individual words instead of the phrase. |
| Search for | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Two or more words in the same topic |
|
|
| Either word in a topic |
|
|
| Topics that do not contain a specific word or phrase |
|
|
| Topics that contain one string and do not contain another | ^ (caret) |
cat ^ mouse
|
| A combination of search types | ( ) parentheses |
|
- System Security
- Encryption of configuration file settings
- Encryption of operator passwords
- Encryption of client keystore passwords
- Randomly generated master keys
- Inactivity timer
- Lockout feature
- System quiesce: Login restrictions
- Mandanten file security
- Multicompany mode
- Script utilities
- Security tables
- Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) encryption and server certificates
- TLS 1.2 Support and Configuration
- Trusted sign-on
- Common Access Card (CAC) sign-on
- SAML Single Sign-On
- FIPS mode
- Tokenization
SAML Single Sign-On
Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) is an XML-based, open-standard data format for exchanging authentication and authorization data between parties, in particular, between an Identity Provider (IdP) and a Service Provider (SP). SAML 2.0 is the industry standard way to federated identity management based on Single Sign-On (SSO). SSO is a session or user authentication process that permits a user to enter the same name and password to access multiple web applications.
As of version 9.50, Service Manager (SM) supports SP-initiated web browser SSO using the SAML 2.0 protocol. The SAML 2.0 specification defines an exhaustive list of profiles. By leveraging HPE Identity Manager (IdM), SM can support two essential profiles: Web Browser SSO Profile, and Single Logout Profile.
When SAML SSO is enabled, if SM and multiple other HPE applications share the same IdP and LDAP Server (no matter whether the other applications leverage IdM or not), the user needs to enter a user name and password only once to log in to all of these web applications. Additionally, this solution supports single logout for multiple HPE web applications that leverage IdM.
Note SAML SSO is supported for the SM Web Tier client, SRC, and Mobility Client. By default, SAML SSO is disabled in Service Manager, and Service Manager clients (Web Tier, Windows, Service Request Catalog (SRC), Mobility, and web services) log in to the Service Manager Server in the same way as before.
Caution Service Manager 9.50 introduces a new end user portal, that is, Service Manager Service Portal. Be aware that SAML SSO is not supported for Service Manager Service Portal. If you are already using or planning to use Service Manager Service Portal as an end user portal, you are not recommended to enable SAML SSO.
The following are some benefits of using this solution:
- Provides tighter security controls through consistent enforcement of security policies across all applications
- Reduces turnaround time for provisioning and deprovisioning of user accounts in applications
- Fosters identity data collection, access reviews, and security analytics
- Provides single sign-on experience for end users
- Enables new users to gain faster access to the resources needed to perform their jobs
- Eliminates or reduces duplicate user IDs
Note Enabling SAML SSO may slow down user logins. According to laboratory tests by HPE, user logins may take approximately 15% more time.
This solution also provides backward compatibility with the legacy LW-SSO solution, and works fine in FIPS mode.
See the following descriptions for more details about this solution.
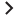
The following diagram illustrates the Web Browser SSO process of Service Manager. In this process, the IdM service acts as an SP to the IdP.
Note Currently, Microsoft Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS) is the only supported IdP. Additionally, ADFS must be configured to authenticate users stored in an LDAP server.
The SM client (Web Tier, SRC, or Mobility Client) uses a built-in IdM client as a filter to obtain an "IdM access token" from the IdM service and then passes the token to the SM Server. The SM Server then validates the IdM access token.
Note LDAP authentication is replaced by IdM; however, the LDAP data mapping is retained in the SM Server.
The following table further explains each step in this process.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | When the user launches the SM client (Web Tier, SRC, or Mobility Client) web URL in the browser, the IdM Client embedded in the SM client sends a request to the IdM service for a request token. |
| 2 | The IdM service returns a response along with a request token to the built-in IdM client of the SM client (SM Web Tier, SRC, or Mobility Client). |
| 3 | The IdM client redirects the request to the IdM service along with that token, and the IdM service then redirects it to the IdP login page with a SAML request. |
| 4 |
The user enters a user name and password to log in to SM from the IdP login page. Note Users log in to Service Manager through the IdP page, and their IdP login name is determined by the IdP. That is, users need to enter their login name using the format required by the IdP. For example, when ADFS is used as the IdP, the login name must be either "userPrincipalName" (xxx@xxx.com) or "domain\samAccountName". |
| 5 |
The IdP redirects the request to the IdM service with a SAML response, and then the IdM service redirects the request to the SM client (Web Tier, SRC, or Mobility Client) along with an "Access Token". Additionally, the IdM service writes a cookie named LWSSO_COOKIE_KEY to the browser. |
| 6 | The SM client (Web Tier, SRC, or Mobility Client) logs in to the SM Server with that "Access Token". |
| 7 |
The user is logged in to SM. |
The SAML SSO solution supports single logout for HPE web applications that leverage HPE Identity Manager (IdM). Once logged out of one application, the user is automatically logged out of the rest of the applications. This single logout behavior applies to the SM web tier, SRC, and Mobility Client.
The SM Windows client, web service clients, and the SRC tablet are not browser-based applications. Login to SM from these clients is referred to as "non-browser login", which does not support SAML. These clients log in to the SM Server through either a password or a token. The token is an LW-SSO token when using the legacy LW-SSO solution or an IdM token when using the IdM solution.
- For password login, the login logic is same as before. That is, the login process does not involve IdM.
- For LW-SSO token login, the SM Server provides a new interface for third- party applications to log in to SM using an IdM access token. The SM Server adds a new http header named “X-Idm-Token”, which contains the string value of the IdM access token.
Users must enter their login name that is determined by the LDAP field mapping on the SM side. For example, if the name field in the SM operator table is mapped to the samAccountName field in ADFS, users must enter their samAccountName value as the login name.
The SAML SSO solution is compatible with the legacy LW-SSO solution.
- Do not enable both SAML SSO and LW-SSO in the Service Manager web tier, SRC, or Mobility Client. The <idm-service>\WEB-INF\hpssoConfig.xml file already includes LW-SSO settings (domain, initString, and lwsso tenant) for compatibility with LW-SSO. For more information about these settings in the IdM service, see Install and configure the HPE Identity Manager service.
- The Service Manager Server can have both SAML SSO and LW-SSO enabled if needed. This is to allow other HPE applications to access the SM Server through LW-SSO when necessary.
Integrations
If SAML SSO is enabled in Service Manager and another HPE application has legacy LW-SSO enabled (or vise versa), users can access either product from the other product side without the need to enter a user name and password.
Note For LW-SSO compatibility, the following limitations apply:
- HPE applications using legacy LW-SSO must share the same LDAP server with Service Manager.
- HPE applications using legacy LW-SSO and Service Manager (Server, Web tier, SRC, and Mobility) must be in the same domain as IdM. This is because IdM needs to read the cookie written by the applications)
To provide the LW-SSO compatibility, the login name in the LW-SSO token must be the same as the login name that is carried in the SAML assertion. This can be achieved through configuration:
- The login name in the LW-SSO token can be configured in the legacy LW-SSO application. For example, for SM, map the name field in the operator table to the samAccountName field in ADFS.
- The login name that is carried in the SAML assertion can be configured in the IdP. For example, in ADFS, click Edit Rule, and NameId field to samAccountName. For detailed steps, see Install and configure the HPE Identity Manager service.
If a user logs in to a legacy LW-SSO application first before logging in to SM, a user object for the user may not already exist in IdM. IdM requires a user object to exist before a user can log in to it through LW-SSO. In this case, the user needs to log in to the IdP first, and then a user object is created in IdM. Once a user object is created in IdM, the user does not need to enter the password again.
If a legacy LW-SSO application uses a dedicated integration user to log in to SM, the integration user must already exist in IdM. You can either add the integration user to the LDAP directory service or add the user to the IdM database directly.
SM Collaboration
In standard mode, SM Collaboration requires LW-SSO to be enabled for the Service Manager Server, web tier, and Chat Server.
If SAML SSO is enabled for the Service Manager Server and web tier, you must enable LW-SSO only for the SM Server and Chat Server. Do not enable LW-SSO for the SM web tier.
Caution You must not enable both SAML SSO and LW-SSO in the web tier. However, you can enable both in the Service Manager Server if needed.
For details, see Install Service Manager Collaboration.
Service Manager Service Portal
Service Manager Service Portal requires LW-SSO to be enabled in both the Service Manager Server and Service Manager Service Portal, no matter whether the Server is running in standard mode or SAML SSO mode. For more information, see Install Service Manager Service Portal.
When FIPS mode is enabled in Service Manager (including the Server, web tier, SRC, and Mobility Client), you need to enable FIPS mode for the IdM service before you can use SAML SSO. In FIPS mode, SAML SSO works correctly using a FIPS compliant data encryption algorithm and Java security provider.
For information about how to enable FIPS mode for the IdM service, see Configure FIPS mode in the IdM Service.
We welcome your comments!
To open the configured email client on this computer, open an email window.
Otherwise, copy the information below to a web mail client, and send this email to ovdoc-ITSM@hpe.com.
Help Topic ID:
Product:
Topic Title:
Feedback: