Searching the Help
To search for information in the Help, type a word or phrase in the Search box. When you enter a group of words, OR is inferred. You can use Boolean operators to refine your search.
Results returned are case insensitive. However, results ranking takes case into account and assigns higher scores to case matches. Therefore, a search for "cats" followed by a search for "Cats" would return the same number of Help topics, but the order in which the topics are listed would be different.
| Search for | Example | Results |
|---|---|---|
| A single word | cat
|
Topics that contain the word "cat". You will also find its grammatical variations, such as "cats". |
|
A phrase. You can specify that the search results contain a specific phrase. |
"cat food" (quotation marks) |
Topics that contain the literal phrase "cat food" and all its grammatical variations. Without the quotation marks, the query is equivalent to specifying an OR operator, which finds topics with one of the individual words instead of the phrase. |
| Search for | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Two or more words in the same topic |
|
|
| Either word in a topic |
|
|
| Topics that do not contain a specific word or phrase |
|
|
| Topics that contain one string and do not contain another | ^ (caret) |
cat ^ mouse
|
| A combination of search types | ( ) parentheses |
|
The NNMi Causal Engine and Object Status
[ This Topic contains tables with hard-coded column width <col style="width: 93px;" /> on the first column. Do not remove those settings. ]
The Causal Engine sets the Status on relevant network objects. Status indicates the overall health of an object and is determined from the outstanding Conclusions. Every Conclusion has a Severity associated with it. The Status reported is the most severe of all outstanding Conclusions. In addition, Conclusions inform the user of the underlying cause (or reason) for an object's Status.
See the Conclusion Tab information for each object form in Accessing Device Details for information about possible Conclusions for each NNMi object.
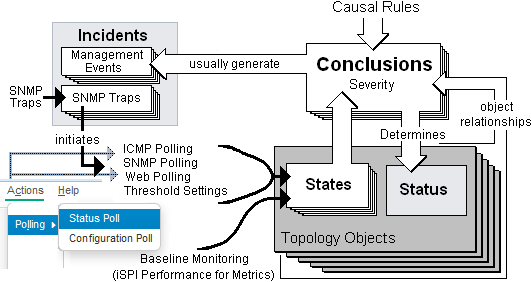
When determining object status for all objects except Node Groups, the Causal Engine uses the most severe Conclusion for the object. Possible Status categories in decreasing order of severity are as follows:
![]() Unknown
Unknown
![]() Disabled
Disabled
![]() Critical
Critical
![]() Major
Major
![]() Minor
Minor
![]() Warning
Warning
![]() Normal
Normal
![]() No Status
No Status
Node Groups only. By default, NNMi propagates the most severe Status of all Node Group Members to the Node Group Status. When propagating Node Group Member Status to the Node Group, the Causal Engine uses the following Status categories in decreasing order of severity. For more information about configuring Node Group Status, see Configure Node Group Status.
![]() Critical
Critical
![]() Major
Major
![]() Minor
Minor
![]() Warning
Warning
![]() Unknown
Unknown
![]() Normal
Normal
![]() No Status
No Status
To determine why an object is not polled (No Status), do the following:
- Select the object from the table or map view and access Actions → Configuration Details → Monitoring Settings.
- Select the node of interest or the node that is hosting the object of interest from the table or map view and access Actions → Configuration Details → Communication Settings.
NNMi analyzes a variety of network objects using either the SNMP protocol or ping to retrieve information about the network object. The following list shows the network objects that NNMi monitors and analyzes. Click each object for more information.
-
 Aggregator Interface (NNMi Advanced)
Aggregator Interface (NNMi Advanced)
An Aggregator Interfaces is a set of interfaces on a switch that are linked together, usually for the purpose of creating a trunk (high bandwidth) connection to another device. Aggregator Interfaces have designated Aggregation Member Interfaces.
NNMi reports that Status of an Aggregator Interface as follows:
 Unknown
UnknownThe Status of all Aggregation Members of the Aggregator Interface are Unknown.  Critical
CriticalThe Aggregator Interface, or all of the Aggregation Members, or both are operationally down. This means ifOperStatusisdown. Minor
MinorSome Aggregation Members (but not all Aggregation Members) of the Aggregator Interface are operationally down. This means the ifOperStatusisdown. Normal
NormalAll Aggregation Members of the Aggregator Interface are operationally up. This means ifOperStatusisup. No Status
No StatusAll Aggregation Members of the Aggregator Interface are not polled. -
 Aggregator Layer 2 Connection (NNMi Advanced)
Aggregator Layer 2 Connection (NNMi Advanced)
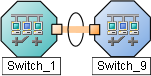
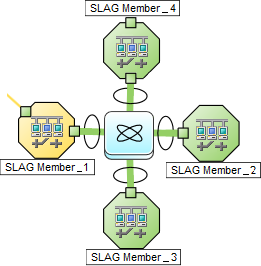
An Aggregator Layer 2 Connection is a connection with endpoints that are Aggregator Interfaces. These are usually high-bandwidth connections that link switches. Aggregator Layer 2 Connections have Aggregator Interfaces and Aggregation Members.
 Click here to see example Link Aggregations.
Click here to see example Link Aggregations.
On a Layer 2 map, a thick line with a superimposed ellipse represents a Link AggregationProtocols used on Switches to configure multiple Interfaces (Aggregation Member Interfaces) to function as if they were one (an Aggregator Interface). When two Aggregator Interfaces establish a connection, that connection is an Aggregator Layer 2 Connection. The Aggregator Layer 2 Connection appears on Layer 2 Neighbor View maps as a thick line with an Interface icon at each end (representing the Aggregator Interface). or Split Link AggregationLink Aggregation with more than two endpoints. Some vendors refer to this as Multi-Chassis Link Aggregation, SLAG, MLAG, or MC-LAG. (group of multiple Layer 2 Connections that are functioning as one). The icon representing an Interface at either end of the thick line is an Aggregator Interface (a logical interface comprised of many physical interfaces that are functioning as one).
Two endpoints:
Three endpoints:
More than three endpoints:
NNMi reports the Status of an Aggregator Layer 2 Connection as follows:
 Unknown
UnknownThe Status of any Aggregation Member of the Aggregator Layer 2 Connection is Unknown.  Critical
CriticalThe Aggregator Interface, the Aggregation Member, or both are operationally down. This means ifOperStatusisdown. Minor
MinorSome Aggregation Members, but not all, are operationally down. This means ifOperStatusisdown. Normal
NormalAll Aggregation Members of the Aggregator Layer 2 Connection are operationally up. This means ifOperStatusisup. No Status
No StatusAll Aggregation Members of the Aggregator Layer 2 Connection are not polled.
-
 Card
Card
A card is a physical component on a device which generally has physical ports that contain one or more interfaces used to connect to other devices. A card can also contain sub-cards. The card containing another card is known in NNMi as the Parent Card. The sub-card is known as a Daughter Card. NNMi supports Daughter cards one level deep.
NNMi reports the status of a Card as follows:
 Unknown
UnknownIndicates the SNMP Agent associated with the Card does not respond to SNMP queries.  Disabled
DisabledThe Card or Child Card is administratively down or disabled. This means the cardAdminStatusisdown. Critical
CriticalThe Card is operationally down. This means the cardOperStatusisdown. Minor
MinorThe Card is neither up nor down. This means the cardOperStatusisunknownorother. Normal
NormalThe Card is operationally up. This means the cardOperStatusisup. No Status
No StatusThe Card is not polled.
-
 Card Redundancy Group
Card Redundancy Group
A Card Redundancy Group is a set of card modules that are configured to provide card redundancy on the device. These cards are management modules on Cisco and s Procurve platforms. The number of cards supported in a group on both platforms is two. The Card Redundancy Group has one card acting as the primary member, the other acting as the secondary. If the primary card fails, the secondary card takes over as the primary card.
NNMi reports the Status of Card Redundancy Groups as follows:
 Unknown
UnknownAll cards in the Card Redundancy Group have an Unknown Status.  Critical
CriticalIndicates either of the following:
- No Card is acting as the Primary member of the Card Redundancy Group.
- Both Cards are acting as the Primary member of the Card Redundancy Group.
 Major
Major At least one card in the group is reporting a state that indicates it is neither the Primary nor Secondary card.  Warning
WarningThe Card Redundancy Group has no Secondary member.  Normal
NormalThe Card Redundancy Group is functioning correctly.  No Status
No StatusNo Status - The Card Redundancy Group has not yet been discovered or is not being polled.
-
 Chassis
Chassis
A Chassis is a physical component on a device into which other objects are plugged, such as cards. A Chassis can also contain sub-chassis. The Chassis containing another Chassis is known in NNMi as the Parent Chassis. The sub-chassis is known as the Child Chassis. A Child Chassis can be one-level deep.NNMi supports the following scenarios:A single node running on one chassisMultiple nodes running on one chassis A single node running on multiple chassisChassis are connected by Inter Switch Links (ISL). A port used for the Inter Switch Link is designated with the Type IRF physical port and is associated with the card or chassis on which it resides.
NNMi reports the status of a Chassis as follows:
 Unknown
UnknownIndicates the SNMP Agent associated with the Chassis does not respond to SNMP queries.  Critical
CriticalThe Chassis is operationally down. This means the operStatusisdown. Major
Major The Chassis operStatusis notdown, and all cards in the chassis have thecardOperStatusofdown. Minor
MinorThe Chassis operStatusis notdown, and more than one card but not all cards have thecardOperStatusofdown Warning
WarningThe Chassis operStatusis notdown, and one card in the chassis has thecardOperStatusofdown. Normal
NormalThe operStatusof the chassis isup, and all cards in the chassis have thecardOperStatusofup. No Status
No StatusThe chassis and all of its cards are not polled.
-
 Chassis Redundancy Group
Chassis Redundancy Group
A Chassis Redundancy Group is a set of chassis that are configured to provide redundancy (for example, for switches). Each redundancy group member is discovered as a Chassis managed by a node. Each Chassis Redundancy Group member has one of the following roles:
- Master - Indicates the chassis is the master member of the Chassis Redundancy Group.
- Slave - Indicates the chassis is a slave member of the Chassis Redundancy Group.
NNMi reports the status of Chassis Redundancy Groups as follows:
 Major
Major No Chassis in the Chassis Redundancy Group has a standby State value of SLAVE.  Minor
MinorIndicates either of the following:
- At least one of the Inter Switch Links (ISL) between the Chassis in the Chassis Redundancy Group is down.
-
NNMi determined the following:
- One Chassis has a MASTER State
- One Chassis has a SLAVE State
- Other Chassis in the group are not in SLAVE State
 Warning
WarningAt least one of the Inter Switch Links (ISL) between the Chassis in the Chassis Redundancy Group is degraded.  Normal
NormalThe Chassis Redundancy Group is functioning correctly.  No Status
No StatusThe Chassis Redundancy Group is not being polled.
-
 Connections
Connections
Connections are Layer 2 physical connections and Layer 3 network connections. NNMi discovers connection information by reading forwarding database (FDB) tables from network devices and gathering data from a variety of Layer 2 discovery protocols (see the list of Topology Source protocols in Layer 2 Connection Form).
NNMi reports the Status of Layer 2 physical connections as follows:
 Unknown
UnknownAll endpoints of the connection have unknown status.  Disabled
DisabledAny one endpoint of the connection is disabled.  Critical
CriticalAll endpoints are operationally down.  Minor
MinorAny one endpoint is down.  Warning
WarningEndpoints have unknown and non-critical Status.  Normal
NormalAll endpoints are operationally up.  No Status
No StatusAll endpoints are not polled. Note
- Pseudo interfaces do not affect Connection Status.
- Connections on Layer 3 maps never have status.
-
 Field Replaceable Units (FRU Card)
Field Replaceable Units (FRU Card)
A Field-Replaceable-Unit (FRU) card is a card that can be replaced on a device that is operationally active (not powered down). When an FRU card is removed from or added to the device, NNMi reports the occurrence with an incident. If an FRU card is not recognized by the device, NNMi reports the unrecognized card with an incident.
NNMi reports the Status of an FRU Card as follows:
 Unknown
UnknownIndicates either of the following:
- The SNMP Agent associated with the card does not respond to SNMP queries.
- NNMi cannot determine the
cardOperStatusorcardAdminStatusvalues.
 Disabled
DisabledThe Card is administratively down. This means the cardAdminStatusisdown. Critical
CriticalThe Card is operationally down. This means the cardOperStatusisdown. Minor
MinorThe Card is neither up nor down. This means the cardOperStatusis eitherunknownorother. Normal
NormalThe Card is operationally up. This means the cardOperStatusisup. No Status
No StatusThe Card is not being polled. -
 Interface
Interface
An interface is a logical object that can be physical or virtual. Interfaces are used to identify connections between nodes. For example, the interface might represent a physical port, a virtual port, or an uplink provided by a hypervisorThe virtual machine manager in charge of delegating various aspects from a pool of resources to become virtual devices. The delegations might be static or dynamic, depending on the manufacture's implementation. The type of virtual machines being generated depends on the manufacturer's implementation..
NNMi also uses Interfaces to represent virtual switches in network environments using hypervisor hosts. Also see Virtual Switch.
Multiple interfaces can be associated with a single port. NNMi identifies interfaces using either of the following values:
- ifName
- ifAlias
- ifType[ifIndex] (for example, ethernetCsmacd[17])
Each port managed by NNMi is associated with one or more interfaces. NNMi identifies ports using the <Card-number / Port-number> value.
NNMi reports the Status of Interfaces as follows:
 Unknown
UnknownIndicates either of the following:
- The SNMP Agent associated with the interface does not respond to SNMP queries.
- The Web Agent associated with the interface does not respond to the management protocol queries specified for the device.
- NNMi cannot determine the health because
ifAdminStatusandifOperStatuscannot be measured.
 Disabled
DisabledIndicates either of the following:
- Interface is administratively down. This means
ifAdminStatusisdown. - The virtual port or interface is associated with a virtual machine that is either turned off or paused.
 Critical
CriticalInterface is operationally down. This means ifOperStatusisdown. Normal
NormalInterface is operationally up. This means ifOperStatusisup. No Status
No StatusInterface is not polled. -
 IP Address
IP Address
An IP address is a routable address that responds to ICMP. IP addresses are typically associated with nodes.
NNMi reports the status of a IP Addresses as follows:
 Disabled
DisabledThe interface associated with this IP address is administratively downordisabled. Critical
CriticalIP address does not respond to ICMP queries (ping the device).  Normal
NormalIP address responds to ICMP queries.  No Status
No StatusIP address is not polled. -
 Node
Node
NNMi typically manages network nodes, reporting Status as follows:
 Unknown
UnknownIndicates the node is unresponsive due to either of the following circumstances:
- The SNMP Agent associated with the node does not respond to SNMP queries and the polled IP addresses do not respond to ICMP queries
- The polled IP addresses associated with the non-SNMP node does not respond to ICMP queries
Additionally:
- If a Web Agent is configured for the node, the Web Agent also does not respond to the management protocol queries specified for the device.
 Disabled
DisabledIndicates a neighbor interface has been disabled, causing the node to be unreachable.
 Critical
CriticalIndicates any one of the following:
- The node is down as determined by neighbor analysis.
- The node is marked as important and is unresponsive (NNMi cannot access the node from the NNMi management server).
- The node is unconnected (it has no neighbors) and, therefore, is unresponsive.
- NNMi cannot determine if the node is down or if the incoming connection is down.
- At least one Custom Polled Instance associated with the node has a Status of Critical and Custom Polled Instances are configured to affect Node Status.
 Minor
MinorA managed object in the Node has any of the following problems:
- The SNMP Agent associated with the Node does not respond to SNMP queries.
- The Web Agent associated with the Node does not respond to the management protocol queries specified for the device.
- The management address on the Node is not responding to ICMP.
- One or more interfaces on the Node are operationally down. This means
ifOperStatusisdown. - One or more IP addresses on the Node do not respond to ICMP.
- NNMi is unable to measure the Status of one or more Cards on the Node. This means the
cardOperStatusis eitherunknownorother. - At least one Interface on the Node has a threshold outside the range specified for the device.
- At least one Custom Polled Instance associated with the Node has a Status of Minor and Custom Polled Instances are configured to affect Node Status.
- One or more cards in the Node are operationally down. This means
cardOperStatusisdown.
 Warning
Warning A managed object on the Node has any of the following problems:
- At least one Card in a Card Redundancy Group associated with the Node is malfunctioning.
- At least one Custom Polled Instance associated with the Node has a Status of Warning and Custom Polled Instances are configured to affect Node Status.
 Major
MajorIndicates NNMi detected any of the following:
- A fan (Physical Sensor) failure
- A power supply (Physical Sensor) failure
- A backplane (Physical Sensor) failure
- A memory (Node Sensor) failure
- At least one Custom Polled Instance associated with the Node has a Status of Major and Custom Polled Instances are configured to affect Node Status.
 Normal
NormalAll objects associated with the node are operationally up.  No Status
No Status The SNMP Agent or Web Agent, all interfaces, and all IP addresses of the node are not polled. -
 Node Groups
Node Groups
A Node Group is a logical collection of nodes created by an NNMi administrator.
An NNMi administrator can also configure Node Group Status calculations. The out-of-the-box configuration propagates the most severe Status as follows:
 Critical
CriticalAt least one node in the Node Group has Critical Status.  Major
MajorNo nodes have a Critical Status, and at least one node in the Node Group has Major Status.  Minor
MinorNo nodes in the Node Group have Critical or Major Status, and at least one Node in the Node Group has Minor Status.  Warning
WarningNo nodes in the Node Group have Critical, Major, or Minor Status, and at least one Node in the Node Group has Warning Status.  Normal
NormalNo nodes in the Node Group have Critical, Major, Minor, or Warning status, and at least one Node in the Node Group has Normal Status.  Unknown
UnknownNo nodes in the Node Group have Critical, Major, Minor, Warning, or Normal Status, and at least one Node in the Node Group has Unknown Status.  No Status
No StatusAll nodes in the group have No Status. -
 Node Sensor
Node Sensor
Some network devices enable SNMP Agents to monitor certain aspects of ongoing usage such as buffers, CPU utilization, disk utilization, and memory utilization. NNMi administrators can monitor the health of these by configuring node sensors to alert their team members when any of these aspects of operation are marginal or failing.
NNMi reports the status of Node Sensors as follows:
 Critical
CriticalThe monitored node health attribute is not functioning properly.  Normal
NormalThe monitored node health attribute is operating properly.  No Status
No StatusThe node health attribute is not currently being polled. -
 Physical Sensor
Physical Sensor
Some network devices enable SNMP Agents to monitor internal components such as backplane, fan, power supply, temperature guage, and voltage regulator. NNMi administrators can monitor the health of these components by configuring physical sensors to alert their team members when any of these components operate marginally or fail.
NNMi reports the status as follows:
 Critical
CriticalThe monitored Physical Component is not functioning properly.  Normal
NormalThe monitored Physical Component is operating properly.  No Status
No StatusThe Physical Component is not currently being polled. -
 Router Redundancy Groups (NNMi Advanced)
Router Redundancy Groups (NNMi Advanced)
A Router Redundancy Group is a set of routers that are configured to provide redundancy in the network. Such groups use the following two types of protocols:
- Hot standby router protocol (HSRP)
- Virtual router redundancy protocol (VRRP)
Router Redundancy Groups usually have a single device acting as the primary, a single device acting as a secondary, and any number of standby devices. If the primary device fails, the secondary device should take over as primary, and one of the standby devices should become secondary. The router groups employ either the HSRP or VRRP protocol to designate the primary, secondary, and standby routers.
NNMi reports the Status of Router Redundancy Groups as follows:
 Critical
CriticalThe Router Redundancy Group has no acting Primary router.  Major
MajorThe Router Redundancy Group's Primary device is not properly configured (for example, multiple Primary routers exist).  Minor
MinorThe Router Redundancy Group' Secondary device is not properly configured (for example, no acting Secondary router exists).  Warning
WarningThe Router Redundancy Group is functioning, but is in some way degraded.  Normal
NormalThe Router Redundancy Group is functioning properly.  No Status
No StatusThe Router Redundancy Group is not yet fully discovered or populated. -
 SNMP Agent
SNMP Agent
An SNMP agent is a process interacting with the managed node and providing management functions. The SNMP agent is responsible for SNMP communications with the managed node. An SNMP Agent can be associated with one or more nodes.
NNMi reports the Status of SNMP Agents as follows:
 Critical
CriticalSNMP Agent does not respond to SNMP queries.  Minor
MinorThe address associated with the SNMP Agent is not responding to ping.  Warning
WarningA high or abnormal ICMP response time from the NNMi management server to the selected node is reported.  Normal
NormalSNMP Agent responds to SNMP queries.  No Status
No StatusSNMP Agent is not polled. -
 Virtual Switch (NNMi Advanced)
Virtual Switch (NNMi Advanced)
NNMi also uses Interfaces to represent Virtual Switches in hypervisor network environments. When the Interface Form provides details about a Virtual Switch, two additional tabs appear:
- Uplinks
- Virtual Ports
The Virtual Switch is identified with the Virtual Bridge capability.
NNMi reports the Status of Virtual Switches as follows:
 Unknown
UnknownIndicates any of the following:
- The SNMP Agent associated with the interface does not respond to SNMP queries.
- NNMi cannot determine the health because the Administrative State and Operational State cannot be measured.
 Disabled
DisabledAll of the Uplinks on the Virtual Switch have an Administrative State of Down.  Critical
CriticalThe Virtual Switch has an Operational State of Down.  Minor
MinorAll of the Uplinks on the Virtual Switch have an Operational State of Down.  Warning
WarningAt least one Uplink on the Virtual Switch has an Operational State of Down.  Normal
NormalThe Virtual Switch has an Operational State of Up.  No Status
No StatusThe Virtual Switch is not polled.  Web Agent (NNMi Advanced)
Web Agent (NNMi Advanced)
The Web Agent represents a management service running on a device and contains the settings NNMi uses to communicate with the device.
NNMi reports the Status of Web Agents as follows:
 Critical
CriticalWeb Agent does not respond to the management protocol queries specified for the device.  Normal
NormalWeb Agent responds to the management protocol queries specified for the device.  No Status
No StatusWeb Agent is not polled.
Related Topics
We welcome your comments!
To open the configured email client on this computer, open an email window.
Otherwise, copy the information below to a web mail client, and send this email to network-management-doc-feedback@hpe.com.
Help Topic ID:
Product:
Topic Title:
Feedback: