Searching the Help
To search for information in the Help, type a word or phrase in the Search box. When you enter a group of words, OR is inferred. You can use Boolean operators to refine your search.
Results returned are case insensitive. However, results ranking takes case into account and assigns higher scores to case matches. Therefore, a search for "cats" followed by a search for "Cats" would return the same number of Help topics, but the order in which the topics are listed would be different.
| Search for | Example | Results |
|---|---|---|
| A single word | cat
|
Topics that contain the word "cat". You will also find its grammatical variations, such as "cats". |
|
A phrase. You can specify that the search results contain a specific phrase. |
"cat food" (quotation marks) |
Topics that contain the literal phrase "cat food" and all its grammatical variations. Without the quotation marks, the query is equivalent to specifying an OR operator, which finds topics with one of the individual words instead of the phrase. |
| Search for | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Two or more words in the same topic |
|
|
| Either word in a topic |
|
|
| Topics that do not contain a specific word or phrase |
|
|
| Topics that contain one string and do not contain another | ^ (caret) |
cat ^ mouse
|
| A combination of search types | ( ) parentheses |
|
Sometimes it is useful to monitor Layer 2 Connections in the following categories:
- Point-to-point or point-to-multipoint connections between interfaces.
- Virtual IPv4 tunnel connections within your management domain.
- Connections to remote sites (across a Service Provider's network or a WAN).
- Connections among Provider Edge (PEProvider Edge router. The Internet Service Provider's router that receives your data on the path to your data's final desination. The Customer Edge (CE) router in your network connects to this PE.) devices in the Default Tenant and Customer Edge (CECustomer Edge router. The router in your network that sends data to an Internet Service Provider's router (the Provider Edge) on the path to the data's final desination.) devices in Tenants defined by the NNMi administrator.
NNMi accomplishes this by following special rules for subnets with prefix lengths between 28 and 31. These special rules are called Subnet Connection Rules.
If you configure a Subnet Connection Rule, the rule independently applies to each Tenant. The members of Subnets must be unique Tenant/Node pairs (each Node assigned to only one Tenant). A Subnet Connection Rule can establish a link between the Default Tenant and another Tenant. However, links between two Tenants are not permitted unless one of them is the Default Tenant. See Configure tenants.
These Subnet Connections Rules enable NNMi to draw arbitrary connections on maps where none would otherwise be detected. If the connection is between two nodes, NNMi draws a standard line on maps. For example:
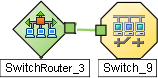
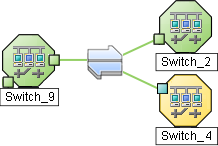
If the connection is between more than two nodes, NNMi displays an ![]() icon (in prior NNMi releases the
icon (in prior NNMi releases the ![]() icon):
icon):
Tip NNMi uses Subnet Connection Rules to prevent incorrect connection calculations to Provider Edge (PE) interfaces. If your network environment includes Provider Edge devices, the following products can provide additional valuable information for your team (click here for more information):
- Network Node Manager iSPI for MPLS Software
-
Route Analytics Management System (RAMS) for MPLS WAN
If you are an NNMi administrator, see RAMS MPLS WAN Configuration (NNMi Advanced) for information about configuring RAMS.
If you double-click the line or the ![]() icon, the Layer 2 Connection form opens and the Topology Source value is
icon, the Layer 2 Connection form opens and the Topology Source value is SUBNETCONNECTION.
NNMi provides a group of predefined Subnet Connection Rules (see Subnet Connection Rules Provided by NNMi). You can edit an existing Subnet Connection Rule or create your own (see Configure Subnet Connection Rules).
If you limit Spiral Discovery to only your Discovery Seeds, NNMi uses the Subnet Connection Rules to detect connections among those devices.
If you use Auto-Discovery rules to configure Spiral Discovery, when NNMi detects a subnet prefix between 28 and 31, NNMi uses the Subnet Connection Rules:
- NNMi checks for an applicable Subnet Connection Rule (see Subnet Connection Rules Provided by NNMi).
-
If a match is found, Spiral Discovery checks the topology database for existing data about each IP address in the subnet. If no data is found for a particular IP address, NNMi issues an SNMP query to the new IP address. The number of available IP addresses for each valid prefix length is described in the following table:
Valid Minimum Prefix Length Values (Subnet Mask Length) Valid Minimum IP Prefix Length Values Number of Usable IPv4 Addresses 28 14 (16-2=14)* 29 6 (8-2=6)* 30 2 (4-2=2)* 31 2 127 2 * Two IP addresses are reserved in each subnet. The first IP address is used for the network itself and the last IP address is reserved for broadcast.
Note A prefix length shorter than 32 is used only for IPv4 subnets and a prefix length longer than 32 is used only for IPv6 subnets.
- NNMi checks the Excluded IP Addresses list. Any addresses in the list are dropped. For details, see Configure an Excluded IP Addresses filter.
- New IP addresses that respond to SNMP are added to the topology database and available for monitoring purposes. New IPv4 addresses that do not respond to SNMP are ignored.
-
If the IP address on each end of a connection has an associated interface, NNMi uses the subnet connection rule to display the connection on map views.
In a Layer 3 Neighbor View map, if NNMi discovers an interface that is connected to more than one interface, the results of your subnet connection rule look like the following:
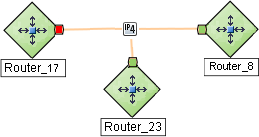
In a Layer 2 Neighbor View map, if NNMi discovers an interface that is connected to more than one interface, the results of your subnet connection rule look like the following:

See Configure Subnet Connection Rules to learn how to configure Subnet Connection Rules.
For details about how Spiral Discovery works: ![]() See Also
See Also
We welcome your comments!
To open the configured email client on this computer, open an email window.
Otherwise, copy the information below to a web mail client, and send this email to network-management-doc-feedback@hpe.com.
Help Topic ID:
Product:
Topic Title:
Feedback:





