Searching the Help
To search for information in the Help, type a word or phrase in the Search box. When you enter a group of words, OR is inferred. You can use Boolean operators to refine your search.
Results returned are case insensitive. However, results ranking takes case into account and assigns higher scores to case matches. Therefore, a search for "cats" followed by a search for "Cats" would return the same number of Help topics, but the order in which the topics are listed would be different.
| Search for | Example | Results |
|---|---|---|
| A single word | cat
|
Topics that contain the word "cat". You will also find its grammatical variations, such as "cats". |
|
A phrase. You can specify that the search results contain a specific phrase. |
"cat food" (quotation marks) |
Topics that contain the literal phrase "cat food" and all its grammatical variations. Without the quotation marks, the query is equivalent to specifying an OR operator, which finds topics with one of the individual words instead of the phrase. |
| Search for | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Two or more words in the same topic |
|
|
| Either word in a topic |
|
|
| Topics that do not contain a specific word or phrase |
|
|
| Topics that contain one string and do not contain another | ^ (caret) |
cat ^ mouse
|
| A combination of search types | ( ) parentheses |
|
[This is the Context-Sensitive Help topic for the Layer 2 Connection form, Aggregation tab.]
The Layer 2 Connection Form provides details about the selected Layer 2 Connection.
For information about each tab: ![]() See Also
See Also
The Layer 2 Connection Form: Link Aggregation Tab appears if the selected connection uses a Link Aggregation protocol.

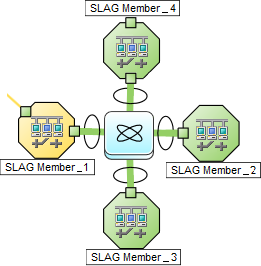
On a Layer 2 map, a thick line with a superimposed ellipse represents a Link AggregationProtocols used on Switches to configure multiple Interfaces (Aggregation Member Interfaces) to function as if they were one (an Aggregator Interface). When two Aggregator Interfaces establish a connection, that connection is an Aggregator Layer 2 Connection. The Aggregator Layer 2 Connection appears on Layer 2 Neighbor View maps as a thick line with an Interface icon at each end (representing the Aggregator Interface). or Split Link AggregationLink Aggregation with more than two endpoints. Some vendors refer to this as Multi-Chassis Link Aggregation, SLAG, MLAG, or MC-LAG. (group of multiple Layer 2 Connections that are functioning as one). The icon representing an Interface at either end of the thick line is an Aggregator Interface (a logical interface comprised of many physical interfaces that are functioning as one).
|
Two endpoints:
|
Three endpoints:
|
More than three endpoints:
|
The selected object's role in the Link Aggregation determines the contents of the tab:
-
Aggregation Member, click here for details.
Attribute Description Link Aggregation Protocol The Link AggregationProtocols used on Switches to configure multiple Interfaces (Aggregation Member Interfaces) to function as if they were one (an Aggregator Interface). When two Aggregator Interfaces establish a connection, that connection is an Aggregator Layer 2 Connection. The Aggregator Layer 2 Connection appears on Layer 2 Neighbor View maps as a thick line with an Interface icon at each end (representing the Aggregator Interface). or Split Link AggregationLink Aggregation with more than two endpoints. Some vendors refer to this as Multi-Chassis Link Aggregation, SLAG, MLAG, or MC-LAG. Protocol currently in use. These protocols allow network administrators to configure a set of interfaces on a switch as one Aggregator Interface, creating an Aggregator Layer 2 Connection to another device using multiple interfaces in parallel to increase bandwidth, increase the speed at which data travels, and increase redundancy:
Text Represents This Protocol Cisco Port Aggregation Protocol Cisco Systems Port Aggregation Protocol (pagp) Nortel Multi-Link Trunking Nortel Multi-Link Trunk technology (mlt) Split MLT Split Multi-Link Trunk: configuration technology (splitMlt) Inter-Switch Trunk MLT Split Multi-Link Trunk: inter-switch trunk (istMlt) 802.3ad Link Aggregation Control Protocol IEEE 802.3ad Link Aggregation Control protocol (LACP) Static/Manual Configured Link Aggregation Static/Manual Configured Link Aggregation Unknown Protocol Link Aggregation unknown It is possible for a Layer 2 Connection to connect sets of Aggregator/Member Interfaces that are configured using different Link Aggregation protocols. In that case, this attribute value contains multiple protocols separated with a slash (/).
nms.topo.core.capability.lag.protocol.PAGP=Cisco Port Aggregation Protocol
nms.topo.core.capability.lag.protocol.MLT=Nortel Multi-Link Trunking
nms.topo.core.capability.lag.protocol.SMLT=Split MLT
nms.topo.core.capability.lag.protocol.ISTMLT=Inter-Switch Trunk MLT
nms.topo.core.capability.lag.protocol.LACP=802.3ad Link Aggregation Control Protocol
nms.topo.core.capability.lag.protocol.STATIC=Static/Manual Configured Link Aggregation
nms.topo.core.capability.lag.protocol.UNKNOWN=Unknown Protocol Link Aggregation
Aggregator Name of the Aggregator that contains the selected participating Aggregation Member:
- Aggregator Interface - represents multiple member interfaces
- Aggregator Layer 2 Connection - thick line on the Layer 2 map represents multiple member Layer 2 Connections
See Layer 2 Neighbor View Map Objects for more information.
Click the
 Lookup icon, and choose
Lookup icon, and choose  Open to open the form for the Aggregator.
Open to open the form for the Aggregator. -
Aggregator (representing multiple members), click here for details.
Attribute Description Link Aggregation Protocol The Link AggregationProtocols used on Switches to configure multiple Interfaces (Aggregation Member Interfaces) to function as if they were one (an Aggregator Interface). When two Aggregator Interfaces establish a connection, that connection is an Aggregator Layer 2 Connection. The Aggregator Layer 2 Connection appears on Layer 2 Neighbor View maps as a thick line with an Interface icon at each end (representing the Aggregator Interface). or Split Link AggregationLink Aggregation with more than two endpoints. Some vendors refer to this as Multi-Chassis Link Aggregation, SLAG, MLAG, or MC-LAG. Protocol currently in use. These protocols allow network administrators to configure a set of interfaces on a switch as one Aggregator Interface, creating an Aggregator Layer 2 Connection to another device using multiple interfaces in parallel to increase bandwidth, increase the speed at which data travels, and increase redundancy:
Text Represents This Protocol Cisco Port Aggregation Protocol Cisco Systems Port Aggregation Protocol (pagp) Nortel Multi-Link Trunking Nortel Multi-Link Trunk technology (mlt) Split MLT Split Multi-Link Trunk: configuration technology (splitMlt) Inter-Switch Trunk MLT Split Multi-Link Trunk: inter-switch trunk (istMlt) 802.3ad Link Aggregation Control Protocol IEEE 802.3ad Link Aggregation Control protocol (LACP) Static/Manual Configured Link Aggregation Static/Manual Configured Link Aggregation Unknown Protocol Link Aggregation unknown It is possible for a Layer 2 Connection to connect sets of Aggregator/Member Interfaces that are configured using different Link Aggregation protocols. In that case, this attribute value contains multiple protocols separated with a slash (/).
nms.topo.core.capability.lag.protocol.PAGP=Cisco Port Aggregation Protocol
nms.topo.core.capability.lag.protocol.MLT=Nortel Multi-Link Trunking
nms.topo.core.capability.lag.protocol.SMLT=Split MLT
nms.topo.core.capability.lag.protocol.ISTMLT=Inter-Switch Trunk MLT
nms.topo.core.capability.lag.protocol.LACP=802.3ad Link Aggregation Control Protocol
nms.topo.core.capability.lag.protocol.STATIC=Static/Manual Configured Link Aggregation
nms.topo.core.capability.lag.protocol.UNKNOWN=Unknown Protocol Link Aggregation
Available Bandwidth
Sum of the interface Input Speed attribute values of the Member Interfaces that have a MIB-II ifOperStatus that is not
Down. If the sum of the interface Output Speed attribute values is different, NNMi displays separate Available Input Bandwidth and Available Output Bandwidth attributes.Maximum Bandwidth Sum of the interface Input Speed attribute values of the Member Interfaces, regardless of MIB-II
ifOperStatus. If the sum of the interface Output Speed attribute values is different, NNMi displays separate Maximum Input Bandwidth and Maximum Output Bandwidth attributes.Available Bandwidth Percentage Percentage value computed using Available Bandwidth divided by the Maximum Bandwidth. Members Table view of the Aggregation Members.
For more information, double-click the row representing an Aggregation Member:
- The Interface Form displays all details about the selected Interface.
- The Layer 2 Connection Form displays all details about the selected Layer 2 Connection.
We welcome your comments!
To open the configured email client on this computer, open an email window.
Otherwise, copy the information below to a web mail client, and send this email to network-management-doc-feedback@hpe.com.
Help Topic ID:
Product:
Topic Title:
Feedback: