Searching the Help
To search for information in the Help, type a word or phrase in the Search box. When you enter a group of words, OR is inferred. You can use Boolean operators to refine your search.
Results returned are case insensitive. However, results ranking takes case into account and assigns higher scores to case matches. Therefore, a search for "cats" followed by a search for "Cats" would return the same number of Help topics, but the order in which the topics are listed would be different.
| Search for | Example | Results |
|---|---|---|
| A single word | cat
|
Topics that contain the word "cat". You will also find its grammatical variations, such as "cats". |
|
A phrase. You can specify that the search results contain a specific phrase. |
"cat food" (quotation marks) |
Topics that contain the literal phrase "cat food" and all its grammatical variations. Without the quotation marks, the query is equivalent to specifying an OR operator, which finds topics with one of the individual words instead of the phrase. |
| Search for | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Two or more words in the same topic |
|
|
| Either word in a topic |
|
|
| Topics that do not contain a specific word or phrase |
|
|
| Topics that contain one string and do not contain another | ^ (caret) |
cat ^ mouse
|
| A combination of search types | ( ) parentheses |
|
- Manage the Number of Incoming Incidents
- Establish Criteria or Relationships for Incoming Incidents
- Correlate Duplicates (Deduplication)
- Deduplication Comparison Parameters Form
- Set Rate (Time Period and Count)
- About Pairwise Configurations
- Incident Pair (Pairwise) Configurations Provided by NNMi
- Configure Pairwise Configurations
- Pairwise Configuration Example
- Rate Comparison Parameters Form
- Suppress Incident Configurations
- Enrich Incident Configurations
- Dampen Incident Configurations
- Configure Custom Correlations
- Establish Criteria or Relationships for Incoming Incidents
Establish Criteria or Relationships for Incoming Incidents
Using NNMi, you can establish the criteria or relationships for the incoming incidents using any of the incident configurations shown in the following diagram. You can choose to use them as is, edit them, or create your own configurations.
Incident Configuration Tabs
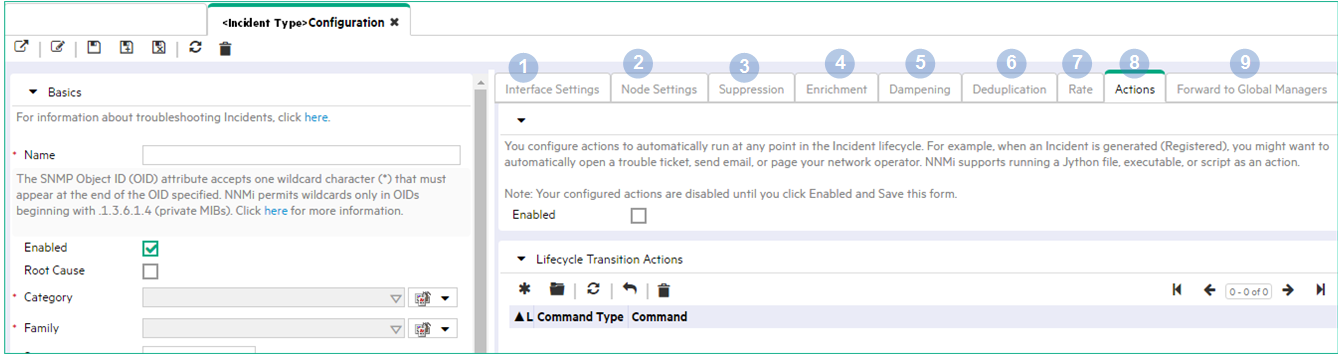
| Configuration Option | When to Use | Example | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Interface Settings | Select this tab to specify that you want to configure Suppression, Enrichment, Dampening, and Actions for a specified Interface Group. |
Change the Severity and Message of an incident configuration for a specified Interface Group. Dampen an Interface Down incident only for the interfaces in a specified Interface Group that you know will be intermittently unavailable. |
| 2 | Node Settings | Select this tab to specify that you want to configure Suppression, Enrichment, Dampening, Actions, and Diagnostic Selections for a specified Node Group. | Change the Severity and Message of an incident configuration for the nodes in a specified Node Group. |
| 3 | Suppression | Select this tab when you want to discard an incident before it appears in an incident view. | Discard an incident if it is in response to a particular status change notification trap. |
| 4 | Enrichment |
Select this tab when you want to fine tune any of the following for a selected incident configuration:
|
Change the Severity and Message of an incident configuration. |
| 5 | Dampening |
Select this tab to delay (dampen) the following for an incident configuration:
|
Lengthen the Dampen Interval for the Interface Down incident Configuration provided by NNMi. Disable Dampening for the Interface Down Incident Configuration provided by NNMi. |
| 6 | Deduplication |
Select this tab to correlate incidents that are identified as duplicates based on one or more Custom Incident Attribute (CIA) or SNMP trap varbind values. To help your operators understand the magnitude or significance of the problem, NNMi tracks the number of duplicates generated. This value is captured as the Duplicate Count attribute. It is incremented on the Duplicate Correlation incident. Its Correlation Nature attribute value is NNMi also records the following information related to duplicate incidents: First Occurrence Time: Indicates the timestamp of the first occurrence of a duplicate incident. Last Occurrence Time: Indicates the timestamp of the latest notification for a set of duplicate incidents. Count: Specifies the number of duplicate incidents for the current configuration that NNMi stores at one time. For example, if the Count is 10, after NNMi receives 10 duplicate incidents, NNMi deletes the first (oldest) duplicate incident and keeps the eleventh. (NNMi stores ten maximum.) Note A Duplicate Correlation incident inherits the Dampening settings of its Correlated Children. If the Correlated Children are Closed while Dampened, and therefore deleted, NNMi retains the parent Duplicate Correlation incident. See Dampening Incident Configurations for more information about Dampening an Incident Configuration. |
Identify any CiscoLinkDown incidents as duplicates if the cia_address value is the same for the incident’s Source Object. |
| 7 | Rate |
Select this tab to measure the rate of incoming incidents within a defined time period and correlate any incidents that occur within the specified time period. NNMi stores the following information related to rate: Count: Indicates the rate at which the incident must occur within the specified timeframe. Hours, Minutes, and Seconds: Used to measure the time within the rate must occur First Occurrence Time: Indicates the time at which the measured rate was reached. Last Occurrence Time: Indicates the last time which the incident occurred. NNMi updates the Correlation Notes with the number of incidents that have occurred within the specified time period. For example, 5 in 5 minutes. Note An incident with a Correlation Nature attribute value of |
If a connection is intermittently down three times within 30 minutes; correlate the Connection Down incidents. |
| 8 | Actions | Select this tab to configure actions to automatically run at any point in the incident lifecycle. For example, you might want to configure an action to occur when an incident of the type you are configuring is generated (Registered). |
When an incident is generated (Registered), open a trouble ticket. After the incident is Closed, close the trouble ticket. |
| 9 | Forward to Global Managers |
(NNMi Advanced - Global Network Management feature) Select the Global Manager Forwarding tab when you want to forward specific SNMP traps from your NNMi management server (a Regional Manager) to all Global Managers in your Global Network Management environment. |
Forward all CiscoLinkDown incidents to the Global Manager. |
You can also create Pairwise Configurations and your own Custom Correlations as described in the table below. See About Pairwise Configurations and Configure Custom Correlations for more information.
| Configuration Option | When to Use | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Pairwise Configurations |
Select the Pairwise Configurations view under the Incidents folder to pair the first occurrence of an incident to another subsequent incident. Note NNMi provides Correlation Notes information only when the Causal Engine has analyzed and Closed the incident. Software that is integrated with NNMi might also provide information identifying the reason an incident was Closed. Any time an incident is Closed manually (for example, by the network operator), NNMi does not provide Correlation Notes information. |
Correlate a CiscoLinkDown incident as the Child Incident for a CiscoLinkUp incident. |
| Custom Correlations |
Select the Custom Correlation Configuration view under the Incidents folder of the When configuring a Custom Correlation, you select the Parent and Child Incident configurations, the time window, and the regular expression that defines the relationship requirements that must be met before the incidents are correlated. |
Correlate Interface Down incidents that occur for subinterfaces under the Interface Down incident generated for the main interface |
See Configure Incidents for more information about the Incident Configuration options. See Load SNMP Trap Incident Configurations for more information about how to specify which SNMP traps you want to receive by automatically creating or updating an incident configuration for an SNMP trap using a MIB file.
Related Topics
We welcome your comments!
To open the configured email client on this computer, open an email window.
Otherwise, copy the information below to a web mail client, and send this email to network-management-doc-feedback@hpe.com.
Help Topic ID:
Product:
Topic Title:
Feedback:





