Searching the Help
To search for information in the Help, type a word or phrase in the Search box. When you enter a group of words, OR is inferred. You can use Boolean operators to refine your search.
Results returned are case insensitive. However, results ranking takes case into account and assigns higher scores to case matches. Therefore, a search for "cats" followed by a search for "Cats" would return the same number of Help topics, but the order in which the topics are listed would be different.
| Search for | Example | Results |
|---|---|---|
| A single word | cat
|
Topics that contain the word "cat". You will also find its grammatical variations, such as "cats". |
|
A phrase. You can specify that the search results contain a specific phrase. |
"cat food" (quotation marks) |
Topics that contain the literal phrase "cat food" and all its grammatical variations. Without the quotation marks, the query is equivalent to specifying an OR operator, which finds topics with one of the individual words instead of the phrase. |
| Search for | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Two or more words in the same topic |
|
|
| Either word in a topic |
|
|
| Topics that do not contain a specific word or phrase |
|
|
| Topics that contain one string and do not contain another | ^ (caret) |
cat ^ mouse
|
| A combination of search types | ( ) parentheses |
|
- Configure Interface Settings for an SNMP Trap Incident
- Configure Incident Suppression Settings for an Interface Group (SNMP Trap Incident)
- Configure Incident Enrichment Settings for an Interface Group (SNMPTrap Incident)
- Configure Custom Incident Attributes to Enrich an Incident Configuration (Interface Settings) (SNMP Trap Incidents)
- Configure a Payload Filter to Enrich an Incident Configuration (Interface Settings) (SNMP Trap Incidents)
- Configure Incident Dampening Settings for an Interface Group (SNMPTrap Incident)
- Configure Incident Actions for an Interface Group (SNMP Trap Incident)
- Configure a Payload Filter for an Incident Action (Interface Settings) (SNMP Trap Incidents)
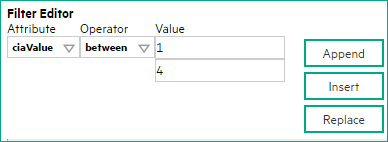
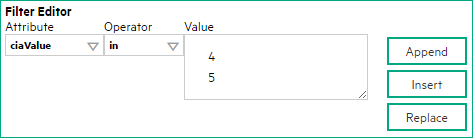
The Payload Filter Editor enables you to create expressions that further refine the filters used to select the incidents to be enriched. Make sure to design any complex Payload Filters offline as a Boolean expression first. This method can help to minimize errors when entering your expressions using the Payload Filter editor.
To create a Payload Filter expression:
-
 Navigate to the SNMP Trap Configuration form:
Navigate to the SNMP Trap Configuration form:
- From the workspace navigation panel, select the Configuration workspace.
- Expand the Incidents folder.
- Select SNMP Trap Configurations.
-
Do one of the following:
- To create an incident configuration, click the
 New icon, and continue.
New icon, and continue. - To edit an incident configuration, select a row, click the
 Open icon, and continue.
Open icon, and continue. - To delete an incident configuration, select a row and click the
 Delete icon.
Delete icon.
- Select the Interface Settings tab.
-
Do one of the following:
- To create a new configuration, click the
 New icon.
New icon. - To edit an existing configuration, select a row, click the
 Open icon, and continue..
Open icon, and continue..
- To create a new configuration, click the
- Make sure you configure the basic Interface Setting behavior. See Configure Interface Settings for an SNMP Trap Incident for more information.
- Select the Enrichment tab.
-
Do one of the following:
- To create an Enrichment configuration, click the
 New icon, and continue.
New icon, and continue. - To edit an Enrichment configuration, select a row, click the
 Open icon, and continue.
Open icon, and continue. - To delete an Enrichment configuration, select a row and click the
 Delete icon.
Delete icon.
- To create an Enrichment configuration, click the
- Make sure the Enrichment settings are configured. See Configure Incident Enrichment Settings for an Interface Group (SNMP Trap Incident) for more information.
- Select the Payload Filter tab.
-
Define your Payload Filter (see table).
- Plan out the logic needed for your Filter String.
-
Use the buttons on the bottom half of the Additional Filters Editor to establish the logic structure.
For example, to establish the following structure, click AND, then AND, and then OR:
(( ) AND ( )) -
Now place your cursor in a location within the displayed Filter String, and use the top half of the filter editor to define the parameters of the highlighted filter requirement.
For example, select a set of parentheses and use the Insert button to specify the filter requirement within those parentheses:
- Click
 Save and Close.
Save and Close. - Click
 Save and Close to save your changes and return to the previous form.
Save and Close to save your changes and return to the previous form.
We welcome your comments!
To open the configured email client on this computer, open an email window.
Otherwise, copy the information below to a web mail client, and send this email to network-management-doc-feedback@hpe.com.
Help Topic ID:
Product:
Topic Title:
Feedback: