Searching the Help
To search for information in the Help, type a word or phrase in the Search box. When you enter a group of words, OR is inferred. You can use Boolean operators to refine your search.
Results returned are case insensitive. However, results ranking takes case into account and assigns higher scores to case matches. Therefore, a search for "cats" followed by a search for "Cats" would return the same number of Help topics, but the order in which the topics are listed would be different.
| Search for | Example | Results |
|---|---|---|
| A single word | cat
|
Topics that contain the word "cat". You will also find its grammatical variations, such as "cats". |
|
A phrase. You can specify that the search results contain a specific phrase. |
"cat food" (quotation marks) |
Topics that contain the literal phrase "cat food" and all its grammatical variations. Without the quotation marks, the query is equivalent to specifying an OR operator, which finds topics with one of the individual words instead of the phrase. |
| Search for | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Two or more words in the same topic |
|
|
| Either word in a topic |
|
|
| Topics that do not contain a specific word or phrase |
|
|
| Topics that contain one string and do not contain another | ^ (caret) |
cat ^ mouse
|
| A combination of search types | ( ) parentheses |
|
Overlapping Address Mapping can help you manage areas in your network that are using address translation protocols, resulting in overlapping and duplicate addresses.
Caution If you are configuring NNMi for areas of your network management domain that use dynamic Network Address Translation (NAT) or dynamic Port Address Translation (PAT/NAPT), the information in this section does not apply.
If static Network Address Translation (NAT) is part of your network management domain, and the NNMi management server is outside of that static NAT domain, you can use Overlapping Address Mapping to configure NNMi for displaying the NAT external IP address (public address). This value appears in the Mapped Address attribute of the IP Address form for the identified Tenant / NAT internal IP address pair. This configuration setting is also important for node monitoring,
Your network domain's static NAT configuration might apply to public IP addresses, private IP addresses, or both.
Network administrators use address translation protocols as a strategy in the following situations:
- When preventing direct Internet access to increase security.
- When not enough public IPv4 addresses are available within their network domain. Packets from the private IP address range are not permitted on the public Internet unless they pass through a protocol that converts the private IP address to a valid public address.
To configure NNMi to display the static NAT external IP address in the Mapped Address attribute of the IP Address form for the identified Tenant / NAT internal IP address pair, you must configure each domain as a unique Tenant.
Then do one of the following:
- Use the Overlapping Address Mapping Form.
- Use the command line tool nnmloadipmappings.ovpl.
Tip To see the results of all mappings, use the Inventory: IP Addresses (All Attributes) view.
Private IP Address Ranges
The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) and Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA)'s reserved the following IP address ranges for private networks, for example enterprise local area networks (LANs), corporate offices, or residential networks.
IPv4 private address ranges (RFC 1918):
- 10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255 (24-bit block)
- 172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255 (20-bit block)
- 192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255 (16-bit block)
IPv6 private address ranges:
- fc00::/7 address block = RFC 4193 Unique Local Addresses (ULA)
- fec0::/10 address block = deprecated (RFC 3879)
NNMi can help you manage areas in your network that are configured using address translation protocols, resulting in Overlapping Addresses / Duplicate Address Domains. Each address domain must be assigned to a unique Tenant. Spiral Discovery requires a Discovery Seed (Tenant / Address pair) to identify each node before NNMi discovers and monitors that node.
Best Practice: No duplicate Domain Name System (DNS) names.
NNMi helps you manage important devices that are using any of the following address translation protocols. The NNMi configuration requirements vary, depending on the protocol:
- Static Network Address Translation (NAT)
- Dynamic Network Address Translation (NAT)
- Dynamic Port Address Translation (PAT/NAPT)
One NNMi management server can manage one or more static Network Address Translation (NAT) domains, each address domain must be assigned to a unique Tenant.
If static Network Address Translation (NAT) is part of your network management domain, you configure NNMi to display the NAT external IP address (public address) in the Mapped Address attribute of the IP Address form for the identified Tenant / NAT internal IP address (such as private IPv4 address) pair. This configuration setting is also important for node monitoring.
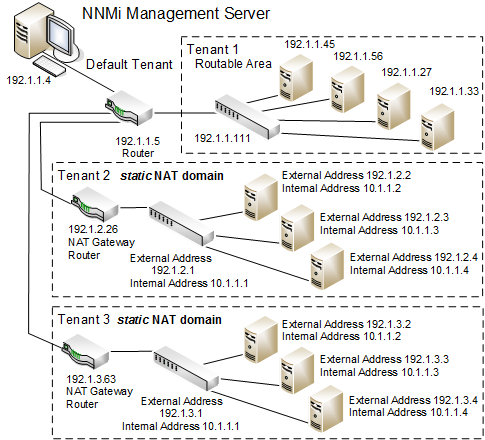
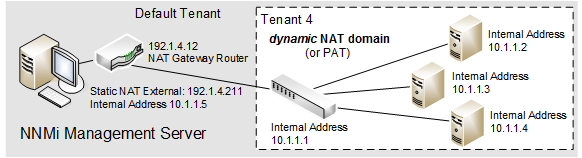
One NNMi management server can manage one dynamic Network Address Translation (NAT) domain or dynamic Port Address Translation (PAT/NAPT) domain. All nodes in this domain must belong to the same Tenant. The NNMi management server must participate in a Global Network Management environment as a Regional Manager.
Use NNMi's Global Network Management feature to monitor multiple dynamic Network Address Translation (NAT), dynamic Port Address Translation (PAT/NAPT) domains, or both. Tenants must be unique within the entire NNMi Global Network Management configuration.
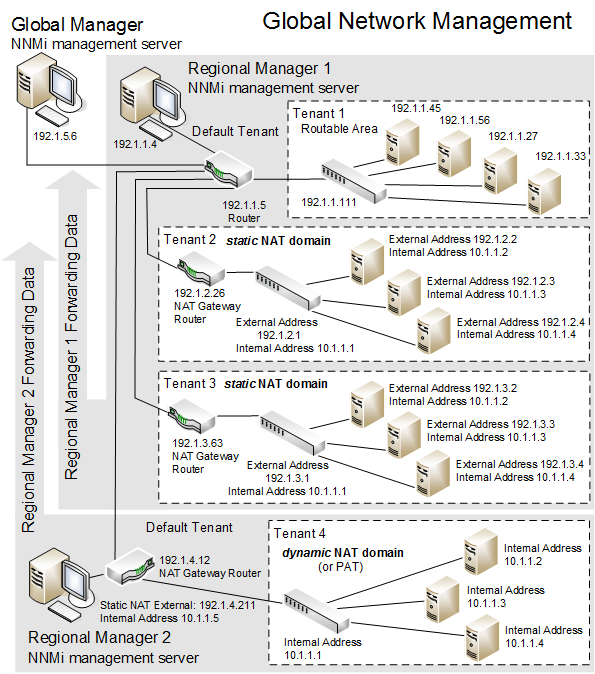
Devices that belong to the Default Tenant can have Layer 2 Connections to any device in any Tenant. Devices within any Tenant other than Default Tenant can have Layer 2 Connections only to devices within the same Tenant or the Default Tenant.
Tip Assign any infrastructure device that interconnects multiple NAT domains (such as a NAT gateway) to the Default Tenant. This ensures that NNMi displays the Layer 2 Connections your team and customers need to see.
Overlapping Address Mapping form
[This is the context-sensitive link for the Overlapping IP Address Mapping form]
If static Network Address Translation (NAT) is part of your network management domain, and the NNMi management server is outside of that static NAT domain, you can use Overlapping Address Mapping to configure NNMi for the following:
- Populate the Mapped Address attribute of the IP Address form for the identified Tenant / NAT internal IP address. This Mapped Address attribute displays the corresponding NAT external IP address (public address).
-
Ensure that in the following special cases, Spiral Discovery successfully detects changes:
- The Communication Configuration you establish for a Node enables the Enable SNMP Address Rediscovery
 attribute. This setting instructs NNMi to search for a new SNMP agent for the Node if the currently configured SNMP agent stops communicating for any reason (rather than waiting for the SNMP agent to come back online).
attribute. This setting instructs NNMi to search for a new SNMP agent for the Node if the currently configured SNMP agent stops communicating for any reason (rather than waiting for the SNMP agent to come back online). - The Monitoring Configuration you establish for a Node enables the Enable IP Address Fault Polling
 attribute. This setting instructs NNMi to use ICMP. When using ICMP for this purpose, the Overlapping IP Address Mapping is required for each monitored internal address within the Static NAT.
attribute. This setting instructs NNMi to use ICMP. When using ICMP for this purpose, the Overlapping IP Address Mapping is required for each monitored internal address within the Static NAT.
- The Communication Configuration you establish for a Node enables the Enable SNMP Address Rediscovery
Your network domains might use static NAT for duplicate addresses in enterprise local area networks (LANs), corporate offices, or residential networks.
If you are configuring NNMi for areas of your network management domain that use dynamic Network Address Translation (NAT) or dynamic Port Address Translation (PAT/NAPT), do not use this form. For more information:
To configure NNMi to display static Network Address Translation (NAT) external IP address in the IP Address form, do the following:
- Prerequisite: Configure each network management domain as a unique Tenant.
-
Navigate to the Overlapping Address Mapping view.
- From the workspace navigation panel, select the
 Configuration workspace.
Configuration workspace.
- Select Discovery.
- Select Overlapping Address Mapping.
- From the workspace navigation panel, select the
-
Do one of the following:
- To create a new configuration, click the
 New icon.
New icon. - To edit an existing configuration, double-click the Overlapping IP Address Mapping definition you want to edit.
- To delete a configuration, select the Overlapping IP Address Mapping definition you want to delete and click the
 Delete icon.
Delete icon.
- To create a new configuration, click the
- Make your configuration choices, all three settings are required.
- Click
 Save and Close.
Save and Close.
If you reassign a Node from one Tenant to another Tenant, this setting does not automatically update.
Related topics
We welcome your comments!
To open the configured email client on this computer, open an email window.
Otherwise, copy the information below to a web mail client, and send this email to network-management-doc-feedback@hpe.com.
Help Topic ID:
Product:
Topic Title:
Feedback:





